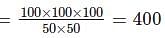KTET Paper 2: Science and Mathematics Test - 10 - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test KTET Mock Test Series 2024 - KTET Paper 2: Science and Mathematics Test - 10
Floor of a square room of side 10 m is to be completely covered with square tiles, each having length 50 cm. The smallest number of tiles needed is
You have given three different tasks to three groups in your classroom -
Group 1: Compare the given figures and find out which one occupies more area.
Group 2: Calculate the perimeter of the given shapes using a ruler.
Group 3: Find out how many steps you can take along the sides of the classroom walls by walking heel to toe.
On what basis have these groups most likely been created?
Group 1: Compare the given figures and find out which one occupies more area.
Group 2: Calculate the perimeter of the given shapes using a ruler.
Group 3: Find out how many steps you can take along the sides of the classroom walls by walking heel to toe.
On what basis have these groups most likely been created?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Aditi wanted to send a secret message to her friend. She gave her friend a letter which did not seems to have anything written on it. She asked her friend to rub the paper with a slice of beet root and the message appeared in dark red colour. Which of the following could she have used to write the message?
A student puts a drop of dilute solution of sodium hydroxide first on a blue litmus paper and then on a red litmus paper. He would observe that
If a cone and a sphere have equal radii and equal volumes, then the ratio between the diameter of the sphere and height of the cone is
The HCF of 1683, 2244 and 5049 is x. The sum of digits of x is
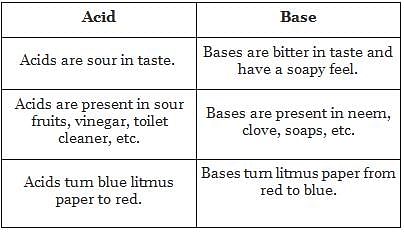
Substance X is used as window cleaner and is basic in nature, while Y is an acid found in grapes. Identify the substances X and Y.
A man, standing between two cliffs, claps his hands and starts hearing a series of echoes at intervals of one second. If the speed of sound in air is 340 ms-1, the distance between the cliffs is _______
If the present age of a father is 42 years and that of his son is 12 years, then what was the ratio of their ages two years ago?
If the energy available to the plants from the sun is 20,000 J, then what would be the energy available to the lion in the food chain, Plant → Dear → Lion?
If you carefully dig a grass plant and observe its roots and leaves you will find that it has
One bell rings for every 6 minutes. Another bell rings every 8 minutes. The third bell rings every 9 minutes. After how many minutes all the three bells will ring together?
The Planet that lies at the outermost orbit of the Solar System is:
A sum of money amounts to Rs. 4,818 after 3 years and Rs. 7,227 after 6 years on compound Interest. The sum is:
Which of the following acids is/are present in acid rain?
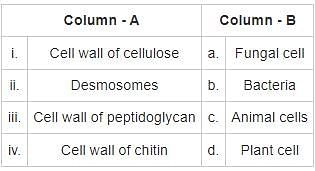
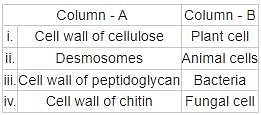
Which of the following pairs is related to the inheritance of characters?
For which kind of problem in mathematics the method of analysis and synthesis is applied?
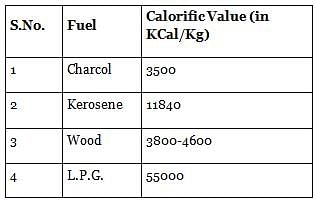
Which one of the following fuels has the maximum calorific value?
"Scientific knowledge is subject to change" This given statement gives which aspect of the nature of science?
Chhaya simplified the given rational number.
This error can be considered as
Which of the following does not reflect the personality attribute of a person having scientific temper?
To analyse the level of questions of a question paper of a Scholastic Achievement Test, useful indices for evaluation are
Giving open-ended tasks in mathematics
In _______ all the cues provided by teacher while teaching, the deductive thinking where in abstract content is differentiated by the teacher giving appropriate examples to the students.
Which is the most appropriate problem solving strategy in a constructivist Mathematics classroom?
In order to enhance the self-esteem of students, they should be allowed to
You have two test tubes 'A' and 'B'. Test tube 'A' contains paste of turmeric, whereas test tube 'B' contains aqueous solution of phenolphthalein. On adding a few drops of dilute hydrochloric acid to these test tubes, the contents of
|
100 tests
|