Level 3 Test: Biological Classification - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Level 3 Test: Biological Classification
Escherichia coli is a bacterium which is a common inhabitant of
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which one of the following is not a diatom?
Cellulose is a major component of the cell wall of
Statement 1: Euglena can be considered as a plant due to the presence of chlorophyll.
Statement 2: Euglena cannot be classified based on two-kingdom systems of classification.
Red tides in oceans occur due to presence and rapid growth of
Assertion: Viruses are not considered the organism
Reason: Viruses are nucleoproteins and lack cell organelle, etc.
Which of the following are called amphibians of the plant kingdom?
Sexual reproduction in fungi can occur using:
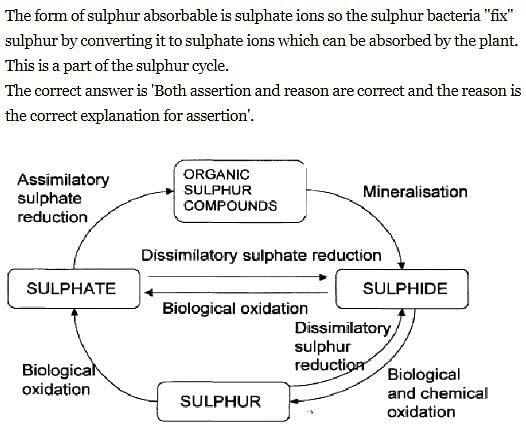
Assertion: Plants absorb sulphur in the form of sulphate ions.
Reason: Sulphur bacteria are required for the formation of sulphate.
The structure(s) found in chlamydomonas but not in amoeba is/are:
Choose the correct answers from the alternatives given. One of the following protists is whirling whips because of the spin produced by two flagella beating in opposing grooves along with their hard-surfaced bodies?