Level- 3 Test: Reproduction in Organisms - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Additional Study Material for NEET - Level- 3 Test: Reproduction in Organisms
Which structure takes part in gametogenesis :
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Organisms such as_____ can regenerate if they are broken into pieces.
Haploid and monoploid numbers of chromosomes of hexaploid wheat are
Self-fertilization occurs in bisexual animals except
Select the mismatched pair out of the following
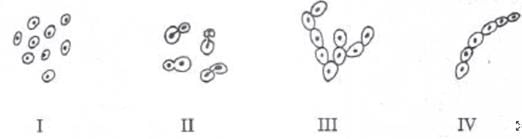
In which of the given figures, budding is not shown?
Self-fertilization occurs in bisexual animals except
Plants like Elm (Ulmus), Dandelion (Taraxacum) and members of Rose Family vegetatively reproduce by
Organisms such as..........can regenerate if they are broken to pieces.
Identify the wrong pair from the following.
Which of the following options shows bisexual animals only?
Read the following statements and select the incorrect one.
A diploid parent plant body produces ________ gametes and a haploid parent plant body produces ________ gametes.
Which of the following organisms has the highest number of chromosomes?
In maize, a meiocyte has 20 chromosomes. What will be the number of chromosomes in its somatic cell?
If a butterfly has chromosome number 360 in its meiocyte (2n). What will be the chromosome number in its gametes?
|
26 videos|287 docs|64 tests
|
|
26 videos|287 docs|64 tests
|

















