MCQ: Analysis (Analytical Reasoning) - 4 - SSC CGL MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - MCQ: Analysis (Analytical Reasoning) - 4
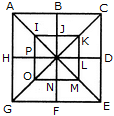
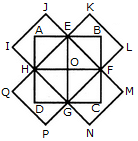
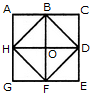
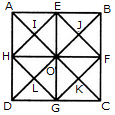
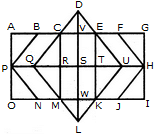
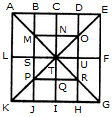
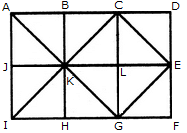
Count the number of triangles and squares in the given figure.
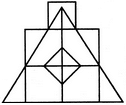

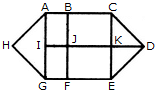
Count the number of parallelogram in the given figure.
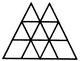

Count the number of parallelogram in the given figure.
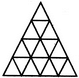

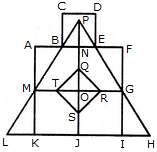
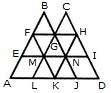
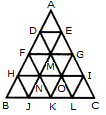
Count the number of triangles and squares in the given figure.
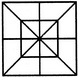
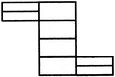
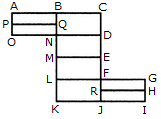
Count the number of rectangles in the given figure.
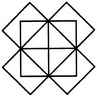
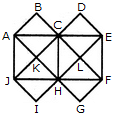
Count the number of convex pentagons in the adjoining figure.
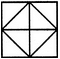
Count the number of triangles and squares in the given figure.
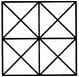
Determine the number of rectangles and hexagons in the given figure.
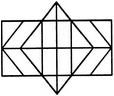
How many rectangles are there in the given figure.
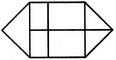
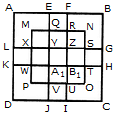
What is the minimum number of straight lines that is needed to construct the figure?
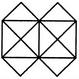
Count the number of squares in the given figure.
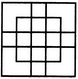
Count the number of squares in the given figure.
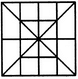
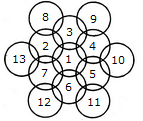
How many circles are there in the adjoining figure.
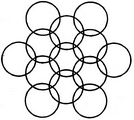
Count the number of squares in the given figure.
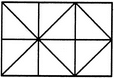
Count the number of rectangles in the given figure.