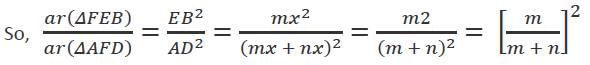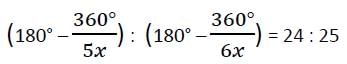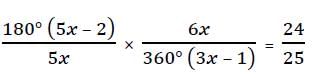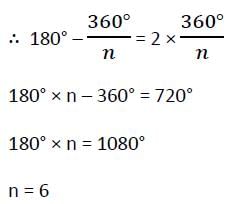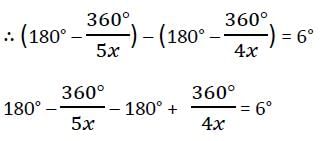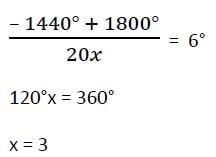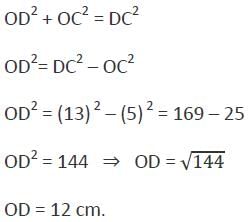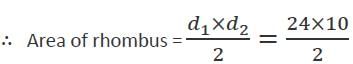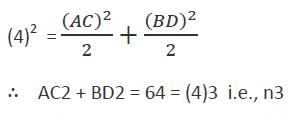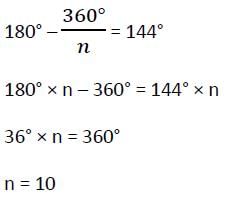MCQ: Quadrilaterals and Polygons - 2 - SSC CGL MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Quantitative Aptitude for SSC CGL - MCQ: Quadrilaterals and Polygons - 2
Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer:
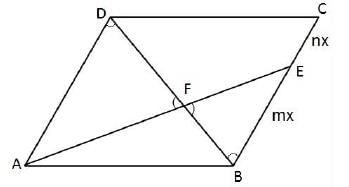
ABCD is a parallelogram. E is a point on BC such that BE : EC = m : n. If AE and DB intersect in F, then what is the ratio of the area of ΔFEB to the area of ΔAFD?
Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer:
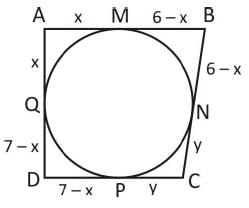
A quadrilateral ABCD circumscribes a circle and AB = 6 cm, CD = 5 cm and AD = 7 cm. The length of side BC is
Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer:
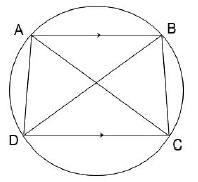
A quadrilateral ABCD is inscribed in a circle. If AB is parallel to CD and AC = BD, then the quadrilateral must be a
Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer:
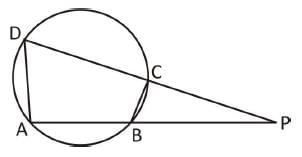
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. AB and DC are produced to meet at P. If ∠ADC = 70° and ∠DAB = 60°, then the ∠PBC + ∠PCB is
Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer:
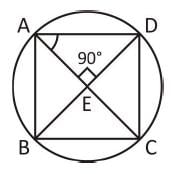
A cyclic quadrilateral ABCD is such that AB = BC, AD = DC, AC ⊥ BD. ∠CAD = Θ. Then the angle ∠ABC =
Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer:
Ratio of the number of sides of two regular polygons is 5 : 6 and the ratio of their each interior angle is 24 : 25. Then the number of sides of these two polygons are
Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer:
Each interior angle of a regular polygon is two times its external angle. Then the number of sides of the polygon is :
Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer:
The diagonals AC and BD of a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD intersect each other at the point P. Then, it is always true that
Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer:
The number of sides in two regular polygons are in the ratio 5 : 4 and the difference between each interior angle of the polygons is 6°. Then the number of sides are
Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer:
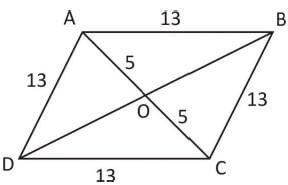
The area of a rhombus with side of 13 cm and one diagonal 10 cm will be
Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer:
ABCD is a quadrilateral such that BC = BA and CD > AD. Which one of the following is correct?
Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer:
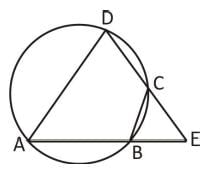
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. The side AB is extended to E in such a way that BE = BC. If ∠ADC = 70°, ∠BAD = 95°, then ∠DCE is equal to
Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer:
Consider the following statements
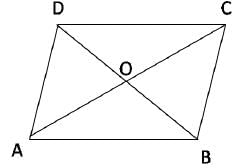
I. Let ABCD be a parallelogram which is not a rectangle. Then, 2(AB2 + BC2) ≠ AC2 + BD2
II. If ABCD is a rhombus with AB = 4 cm, then AC2 + BD2 = n3 some positive integer n.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer:
Each interior angle of a regular polygon is 144°. The number of sides of the polygon is
Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer:
If the sum of the interior angles of a regular polygon be 1080°, the number of sides of the polygon is
|
342 videos|301 docs|185 tests
|