MPTET Varg 2 Science Mock Test - 3 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test MPTET Varg 2 Mock Test Series 2024 - MPTET Varg 2 Science Mock Test - 3
गद्यांश के अनुसार किसकी प्रतिष्ठा अच्छी नहीं थी?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
जंगल का कोई भी जानवर हड्डी निकालने में बाघ की मदद नहीं करना चाहता था क्योंकि ________I
Direction: Fill in the blank with the correct conjunction.
I did not go to the show ______ I had already seen it.
Fill in the blanks with suitable Article from the given alternatives.
Most of ______________ chimneys come with a lifetime warranty offer so that you can enjoy cooking for many years.
Which of the following numbers will replace the question mark (?) in the given series?
90, 89, 85, 76, ?, 35
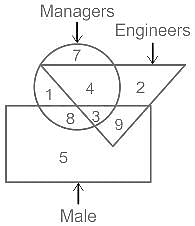
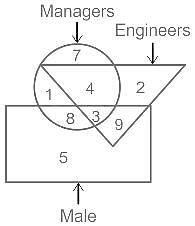
Which of the following numbers in the Venn Diagram represents males who are managers but not Engineers?
The 25th National Volleyball Championship was organized in which district of Madhya Pradesh ?
Meaningful perception of material is essential component of learning. This is a concept of
An object of 5 kg is lying at rest. Under the action of a constant force, it gains a speed of 3 m/s. The work done by the force will be _________.
Which of the following statement is correct?
I. 1 kWh = 3.6 × 106 J.
II. The SI unit of electric current is the ampere.
For the reaction A + 2B → C, 5 moles of A and 8 moles of B will produce
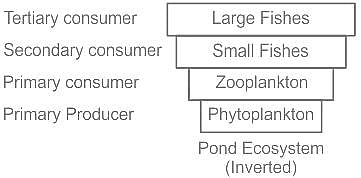
Which of the following ecological pyramid is generally inverted
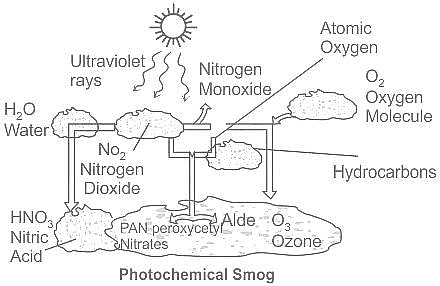
Which of the following is not a common component of Photo-chemical smog?
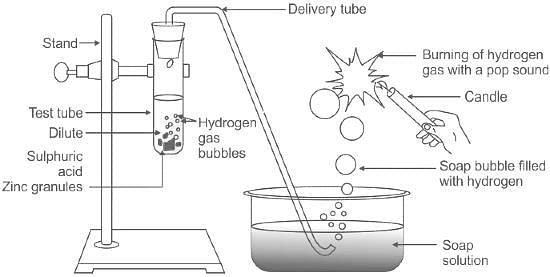
The pop sound occurs on burning the gas obtained after _________
One atmospheric pressure is equivalent to
a) 76 cm of Hg
b) 56 cm Hg
c) 60 cm of Hg
d) 70 cm of Hg
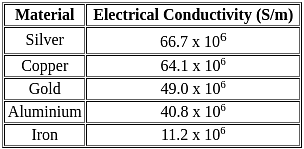
What is the correct sequence of Electrical Conductivity of silver, copper, and gold at room temperature?


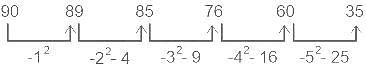
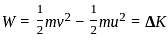

 [ H+ + Ph– ] (Ionised, Pink).
[ H+ + Ph– ] (Ionised, Pink).