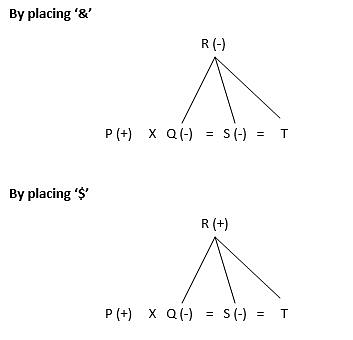NABARD Assistant Manager Grade 'A' Mock Test - 8 - Bank Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test NABARD Assistant Manager Grade A Mock Test Series 2025 - NABARD Assistant Manager Grade 'A' Mock Test - 8
In a lake, there are 10 steps labelled using alphabets from A to J. Starting from step A, every minute a frog jumps to the 4th step from where it started - that is from the step A it would go to the step E and from E it would go to the step I and from I it would go to C etc.
Q. Where would the frog be at the 60th minute if it starts at the step A?
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
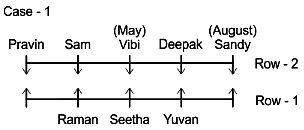
There are Ten persons namely Pravin, Sam, Raman, Seetha, Deepak, Yuvan, Vijay, Sandy, Vibi and Ajith are sitting in two parallel rows containing five people each in such a way that there is an equal distance between adjacent persons. People sitting in Row-1 facing north direction while people sitting in Row-2 facing south direction. Therefore people sitting in Row-1 face the people sitting in Row-2. They were born in following months among January, March, April, May, June, July and August. Exactly two persons were born in each of the month of April, May and June. All the above information is not necessarily in the same order.
Seetha sits exactly in the middle of the north facing row. Deepak sits between Vibi and Sandy and opposite to Yuvan. Pravin sits at the extreme right end of the south facing row. Only one person sits between the two persons who were born in April. Sam sits opposite to Raman and to the immediate right of the person, who was born in May month. Raman doesn’t face south direction. Sandy was born in August month. The person who was born in March sits to the immediate right of Ajith and opposite to the person who is born in April. The person born in January sits to the right of the person born in July but they don’t sit at any of the ends. Only one person sits between the two persons who were born in May.
Q. Which of the following pair is born on same month?
If Football is called Cricket, Cricket is called Basketball, Basketball is called Badminton, Badminton is called Volleyball, Volleyball is called Hockey and Hockey is called Golf, then which of the following games is not played using a ball?
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
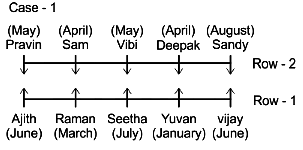
There are Ten persons namely Pravin, Sam, Raman, Seetha, Deepak, Yuvan, Vijay, Sandy, Vibi and Ajith are sitting in two parallel rows containing five people each in such a way that there is an equal distance between adjacent persons. People sitting in Row-1 facing north direction while people sitting in Row-2 facing south direction. Therefore people sitting in Row-1 face the people sitting in Row-2. They were born in following months among January, March, April, May, June, July and August. Exactly two persons were born in each of the month of April, May and June. All the above information is not necessarily in the same order.
Seetha sits exactly in the middle of the north facing row. Deepak sits between Vibi and Sandy and opposite to Yuvan. Pravin sits at the extreme right end of the south facing row. Only one person sits between the two persons who were born in April. Sam sits opposite to Raman and to the immediate right of the person, who was born in May month. Raman doesn’t face south direction. Sandy was born in August month. The person who was born in March sits to the immediate right of Ajith and opposite to the person who is born in April. The person born in January sits to the right of the person born in July but they don’t sit at any of the ends. Only one person sits between the two persons who were born in May.
Q. Four out of the five are similar in certain way and form a group, which of the following does not belong to the group?
Study the following information and answer the given questions
A word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of words and numbers rearranges them following a particular rule. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.
INPUT: while 22 window yells 12 become 36 cost 48 hole 97 73
Step I: become while 22 window yells 12 36 cost 48 hole 97 73
Step II: become 12 while 22 window yells 36 cost 48 hole 97 73
Step III: become 12 cost while 22 window yells 36 48 hole 97 73
Step IV: become 12 cost 22 while window yells 36 48 hole 97 73
Step V: become 12 cost 22 hole while window yells 36 48 97 73
Step VI: become 12 cost 22 hole 36 while window yells 48 97 73
Step VII: become 12 cost 22 hole 36 while 48 window yells 97 73
Step VIII: become 12 cost 22 hole 36 while 48 window 73 yells 97
Step VIII is the last step of the arrangement of the above input as the intended arrangement is obtained.
As per the rules followed in the above steps, find out in each of the following questions the appropriate steps for the given input.
Input: milk 47 simple 75 23 viva 16 sample elf 34
Q. Which of the following would be the final arrangement?
Directions: These questions are based on the following information.
There are 7 family members P, Q, R, S, T, U and V going to a party. There are three generations in which only two are married couples. P is the grandfather of U who is a male. R is the son-in-law of S. V is the son of Q. S has only two children, both of the same gender. T is the sister-in-law of R.
Q. Who is Q in this party?
Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below it.
Few people are sitting in a row facing North. 3 persons are sitting between M and N. K is third to the right of N. K is second to the left of P. Number of person between M and P is same s the number of person between M and L. Only three person sit to the left of L. Six person sits between L and J. Two person sit between P and R. R is sitting at second position from one of the end.
Q. What is the position of J with respect to M?
Directions: These questions are based on the following information.
There are 7 family members P, Q, R, S, T, U and V going to a party. There are three generations in which only two are married couples. P is the grandfather of U who is a male. R is the son-in-law of S. V is the son of Q. S has only two children, both of the same gender. T is the sister-in-law of R.
Q. How many males are there?
In each of the questions below are given some statements followed by some conclusions. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
Only a few suits are pieces.
Some pieces are jute.
All jute are needles.
All needles are threads.
Conclusions:
I. Some suits are not jute.
II. Some threads being suits is a possibility.
III. All pieces are threads.
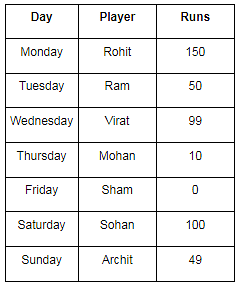
Direction: Study the following instruction carefully and answer the given questions
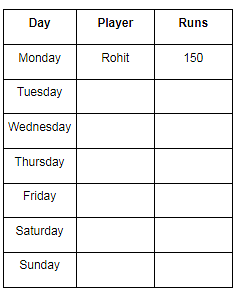
There are 7 cricket players playing on different days of a week and scores different run. Players are Ram, Sham, Mohan, Sohan, Archit, Virat and Rohit. They play from Monday to Sunday not in the same order. The run scored by them is 50, 100, 150, 10, 0, 99 and 49. (The order may be different).
Rohit was the first one to play. Rohit scored the highest run among the all. Archit and Sohan being private employs the played on weekend. Sohan played a day before Archit played. Sham played before Sohan and after Mohan. Mohan played on the mid – day of the week. Ram played 3 days before Sham played. Virat played well but couldn’t complete its century and scored 99 runs. Ram score 1/3 of the runs scored by Rohit. Sum of runs scored by Mohan and Archit is 59. Archit scored more runs than Mohan. Sham scored a duck. (Week starts from Monday)
Q. Who scored a century and when did he play?
Each vowel of the GLADIOLUS word is substituted with the next letter of the English alphabetical series and each consonant is substituted with the letters preceding it. How many vowels will be present in the new arrangement?
Direction: Study the following instruction carefully and answer the given questions
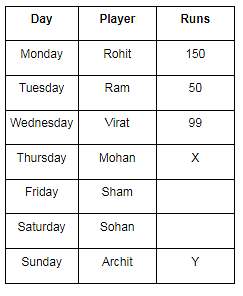
There are 7 cricket players playing on different days of a week and scores different run. Players are Ram, Sham, Mohan, Sohan, Archit, Virat and Rohit. They play from Monday to Sunday not in the same order. The run scored by them is 50, 100, 150, 10, 0, 99 and 49. (The order may be different).
Rohit was the first one to play. Rohit scored the highest run among the all. Archit and Sohan being private employs the played on weekend. Sohan played a day before Archit played. Sham played before Sohan and after Mohan. Mohan played on the mid – day of the week. Ram played 3 days before Sham played. Virat played well but couldn’t complete its century and scored 99 runs. Ram score 1/3 of the runs scored by Rohit. Sum of runs scored by Mohan and Archit is 59. Archit scored more runs than Mohan. Sham scored a duck. (Week starts from Monday)
Q. When did Virat played?
Study the following information carefully and answer the following question given below:
‘X & Y’ means ‘X is mother of Y’
‘X $ Y’ means ‘X is father of Y’
‘X % Y’ means ‘X is daughter of Y’
‘X * Y’ means ‘X is husband of Y’
‘X # Y’ means ‘X is sister of Y’
Q. What should come in place of question mark to establish that P is brother-in-law of S in the given expression?
P * Q % R ? S # T
Direction: Study the information given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Point B is 6 m South of point A. C is 3 m South of B. D is 3 m West of C. E is 5 m North of D. F is 6 m East of E.
Q. In which direction is point C with respect to point F?
Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions.
In a certain code language,
“ offered interest larger disputed ” is written as ‘3V 3F 2H 3V’
“resolve formula central settlement” is written as ‘3U 3Y 2N 3F’
“title harmony mediation appointed” is written as ‘2U 2A 5L 4V’
“alternative inform condition national” is written as ‘5U 2M 4L 4N’
Q. The code ‘2A 2V 3S 2U’ may represent
Direction: Study the information given carefully and answer the question given below.
In a certain code language,
“ram farmer wheat crop” is coded as “Sm3, Gr6, Xt5, Dp4”
“harvest rice corn together” is coded as “It7, Se4, Dn4, Ur8”
“Water plant daily grows” is coded as “Xr5, Qt5, Ey5, Hs5”.
Q. What is the code for “save water enjoy life”?
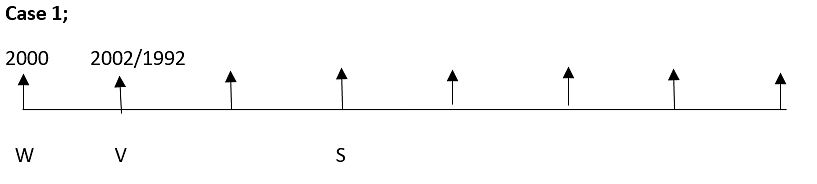
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions below:-
There are eight persons namely, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W born in the same month of different years viz, 1985, 1987, 1990, 1992, 1995, 2000, 2001 and 2002 and all are sitting in a row facing north , but not necessarily in the same order. The age was considered as on the year 2019.
W was born on a leap year and sits at any of the extreme end. W is 5 years younger than S, who sits second to the right of V, born in an even numbered year but not in 1990 and is an immediate neighbour of W. V is 12 years younger than Q, who is 5 years younger than U. There are three persons sitting between V and R, who is 3years older than Q, who is not to the right of R. There are as many persons between V and T is same as P and R. There is one person between U and R. T was not born in the odd numbered year.
Q. Who among the following sits in the exact between of the one who is born in year 1995 and R?
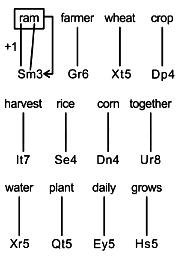
Direction: Study the information given carefully and answer the question given below.
In a certain code language,
“ram farmer wheat crop” is coded as “Sm3, Gr6, Xt5, Dp4”
“harvest rice corn together” is coded as “It7, Se4, Dn4, Ur8”
“Water plant daily grows” is coded as “Xr5, Qt5, Ey5, Hs5”.
Q. “Ng9” may be the code for which of the following words?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions below:-
There are eight persons namely, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W born in the same month of different years viz, 1985, 1987, 1990, 1992, 1995, 2000, 2001 and 2002 and all are sitting in a row facing north , but not necessarily in the same order. The age was considered as on the year 2019.
W was born on a leap year and sits at any of the extreme end. W is 5 years younger than S, who sits second to the right of V, born in an even numbered year but not in 1990 and is an immediate neighbour of W. V is 12 years younger than Q, who is 5 years younger than U. There are three persons sitting between V and R, who is 3years older than Q, who is not to the right of R. There are as many persons between V and T is same as P and R. There is one person between U and R. T was not born in the odd numbered year.
Q. How many persons are sitting between P and the one who is born in the year 1985?
Direction: Study the information given carefully and answer the question given below.
In a certain code language,
“ram farmer wheat crop” is coded as “Sm3, Gr6, Xt5, Dp4”
“harvest rice corn together” is coded as “It7, Se4, Dn4, Ur8”
“Water plant daily grows” is coded as “Xr5, Qt5, Ey5, Hs5”.
Q. “No5” may be the code for which of the following?
Rearrange the following six sentences a, b, c, d, e and f in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph; then answer the questions given below them.
a) The Supreme Court verdict of May 2014 striking down a statutory provision for prior government clearance for a Central Bureau of Investigation probe against officials of the rank of joint secretary and above is the touchstone against which the constitutionality of the pre-investigation sanction requirement will be tested
b) The Union government, too, has a set of amendments to the Prevention of Corruption Act pending since 2013, including a proviso for prior sanction.
c) The court had observed that such a provision destroys the objective of anti-corruption legislation, blocks the truth from surfacing, thwarts independent investigation and forewarns corrupt officers
d) This is the first time a section prescribing punishment for disclosure is being introduced in India, though provisions barring investigation or prosecution without prior sanction are also in force in Maharashtra.
e) Anti-corruption legislation in India seems to be in a state of unacceptable flux.
f) However, the time limit for the sanctioning authority to act is 180 days in Rajasthan, and 90 days in Maharashtra.
Q. Which is the FIRST sentence of the paragraph?
Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
The struggle to achieve gender equality and bridge the gap between men and women is a long and difficult one. India has got another opportunity to do much better for half of its population with the Global Gender Gap Index for 2022, released by the World Economic Forum on Wednesday, placing it at 135 out of 146 countries. But the new data — India’s ranking in 2021 was 140 out of 156 countries — hardly brings cheer as India has fared the worst in at least one of the parameters — ‘health and survival’ — in which it took the last spot. The Global Gender Gap Index benchmarks the current state and evolution of gender parity across four dimensions: economic participation and opportunity; educational attainment; health and survival, and political empowerment. India ranks poorly among its neighbours and is behind Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, the Maldives and Bhutan. Only Iran, Pakistan and Afghanistan perform worse than India in the region. In 2022, coming on the back of a pandemic, war and economic crises, the global gender gap has been closed by 68.1%, which means at the current rate of progress it will take 132 years to reach full parity. Among all the regions, it will take the longest for South Asia to reach the target — 197 years — “due to a broad stagnation in gender parity scores ... in the region”.
There have been enough numbers from the ground to indicate that India, with a female population of approximately 66 crores, has faltered on the road to gender parity. In the pandemic years, as incomes shrank, women faced hurdles on every front, from food, health, and education for the girl child to jobs. The latest NFHS data (2019-2021) show that 57% of women (15-49 age bracket) are anaemic, up from 53% in 2015-16; though 88.7% of married women participate in key household decisions, only 25.4% of women, aged 15-49 years, who worked in the last 12 months (2019-2021), were paid in cash. Women having a bank account or savings account that they themselves use have increased to 78.6%, with schemes such as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana helping, but women's participation in the labour force has shrunk. According to Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE) data, in 2016-17 about 15% of women were employed or looking for jobs; this metric dipped to 9.2% in 2021-22. The best way to improve India’s abysmal ranking is to do it right by women. For that, it is imperative to increase the representation of women in leadership positions at all levels so that women get greater access to jobs and resources. It is up to the Government to move beyond tokenism and help women overcome staggering economic and social barriers.ctions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
The struggle to achieve gender equality and bridge the gap between men and women is a long and difficult one. India has got another opportunity to do much better for half of its population with the Global Gender Gap Index for 2022, released by the World Economic Forum on Wednesday, placing it at 135 out of 146 countries. But the new data — India’s ranking in 2021 was 140 out of 156 countries — hardly brings cheer as India has fared the worst in at least one of the parameters — ‘health and survival’ — in which it took the last spot. The Global Gender Gap Index benchmarks the current state and evolution of gender parity across four dimensions: economic participation and opportunity; educational attainment; health and survival, and political empowerment. India ranks poorly among its neighbours and is behind Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, the Maldives and Bhutan. Only Iran, Pakistan and Afghanistan perform worse than India in the region. In 2022, coming on the back of a pandemic, war and economic crises, the global gender gap has been closed by 68.1%, which means at the current rate of progress it will take 132 years to reach full parity. Among all the regions, it will take the longest for South Asia to reach the target — 197 years — “due to a broad stagnation in gender parity scores ... in the region”.
There have been enough numbers from the ground to indicate that India, with a female population of approximately 66 crores, has faltered on the road to gender parity. In the pandemic years, as incomes shrank, women faced hurdles on every front, from food, health, and education for the girl child to jobs. The latest NFHS data (2019-2021) show that 57% of women (15-49 age bracket) are anaemic, up from 53% in 2015-16; though 88.7% of married women participate in key household decisions, only 25.4% of women, aged 15-49 years, who worked in the last 12 months (2019-2021), were paid in cash. Women having a bank account or savings account that they themselves use have increased to 78.6%, with schemes such as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana helping, but women's participation in the labour force has shrunk. According to Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE) data, in 2016-17 about 15% of women were employed or looking for jobs; this metric dipped to 9.2% in 2021-22. The best way to improve India’s abysmal ranking is to do it right by women. For that, it is imperative to increase the representation of women in leadership positions at all levels so that women get greater access to jobs and resources. It is up to the Government to move beyond tokenism and help women overcome staggering economic and social barriers.
Q. Choose the synonym of the word 'Imperative'.
Rearrange the following six sentences a, b, c, d, e and f in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph; then answer the questions given below them.
a) The Supreme Court verdict of May 2014 striking down a statutory provision for prior government clearance for a Central Bureau of Investigation probe against officials of the rank of joint secretary and above is the touchstone against which the constitutionality of the pre-investigation sanction requirement will be tested.
b) The Union government, too, has a set of amendments to the Prevention of Corruption Act pending since 2013, including a proviso for prior sanction.
c) The court had observed that such a provision destroys the objective of anti-corruption legislation, blocks the truth from surfacing, thwarts independent investigation and forewarns corrupt officers.
d) This is the first time a section prescribing punishment for disclosure is being introduced in India, though provisions barring investigation or prosecution without prior sanction are also in force in Maharashtra.
e) Anti-corruption legislation in India seems to be in a state of unacceptable flux.
f) However, the time limit for the sanctioning authority to act is 180 days in Rajasthan, and 90 days in Maharashtra.
Q. Which is the THIRD sentence of the paragraph?
Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
The struggle to achieve gender equality and bridge the gap between men and women is a long and difficult one. India has got another opportunity to do much better for half of its population with the Global Gender Gap Index for 2022, released by the World Economic Forum on Wednesday, placing it at 135 out of 146 countries. But the new data — India’s ranking in 2021 was 140 out of 156 countries — hardly brings cheer as India has fared the worst in at least one of the parameters — ‘health and survival’ — in which it took the last spot. The Global Gender Gap Index benchmarks the current state and evolution of gender parity across four dimensions: economic participation and opportunity; educational attainment; health and survival, and political empowerment. India ranks poorly among its neighbours and is behind Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, the Maldives and Bhutan. Only Iran, Pakistan and Afghanistan perform worse than India in the region. In 2022, coming on the back of a pandemic, war and economic crises, the global gender gap has been closed by 68.1%, which means at the current rate of progress it will take 132 years to reach full parity. Among all the regions, it will take the longest for South Asia to reach the target — 197 years — “due to a broad stagnation in gender parity scores ... in the region”.
There have been enough numbers from the ground to indicate that India, with a female population of approximately 66 crores, has faltered on the road to gender parity. In the pandemic years, as incomes shrank, women faced hurdles on every front, from food, health, and education for the girl child to jobs. The latest NFHS data (2019-2021) show that 57% of women (15-49 age bracket) are anaemic, up from 53% in 2015-16; though 88.7% of married women participate in key household decisions, only 25.4% of women, aged 15-49 years, who worked in the last 12 months (2019-2021), were paid in cash. Women having a bank account or savings account that they themselves use have increased to 78.6%, with schemes such as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana helping, but women's participation in the labour force has shrunk. According to Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE) data, in 2016-17 about 15% of women were employed or looking for jobs; this metric dipped to 9.2% in 2021-22. The best way to improve India’s abysmal ranking is to do it right by women. For that, it is imperative to increase the representation of women in leadership positions at all levels so that women get greater access to jobs and resources. It is up to the Government to move beyond tokenism and help women overcome staggering economic and social barriers.ctions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct/most appropriate options:
The struggle to achieve gender equality and bridge the gap between men and women is a long and difficult one. India has got another opportunity to do much better for half of its population with the Global Gender Gap Index for 2022, released by the World Economic Forum on Wednesday, placing it at 135 out of 146 countries. But the new data — India’s ranking in 2021 was 140 out of 156 countries — hardly brings cheer as India has fared the worst in at least one of the parameters — ‘health and survival’ — in which it took the last spot. The Global Gender Gap Index benchmarks the current state and evolution of gender parity across four dimensions: economic participation and opportunity; educational attainment; health and survival, and political empowerment. India ranks poorly among its neighbours and is behind Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, the Maldives and Bhutan. Only Iran, Pakistan and Afghanistan perform worse than India in the region. In 2022, coming on the back of a pandemic, war and economic crises, the global gender gap has been closed by 68.1%, which means at the current rate of progress it will take 132 years to reach full parity. Among all the regions, it will take the longest for South Asia to reach the target — 197 years — “due to a broad stagnation in gender parity scores ... in the region”.
There have been enough numbers from the ground to indicate that India, with a female population of approximately 66 crores, has faltered on the road to gender parity. In the pandemic years, as incomes shrank, women faced hurdles on every front, from food, health, and education for the girl child to jobs. The latest NFHS data (2019-2021) show that 57% of women (15-49 age bracket) are anaemic, up from 53% in 2015-16; though 88.7% of married women participate in key household decisions, only 25.4% of women, aged 15-49 years, who worked in the last 12 months (2019-2021), were paid in cash. Women having a bank account or savings account that they themselves use have increased to 78.6%, with schemes such as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana helping, but women's participation in the labour force has shrunk. According to Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE) data, in 2016-17 about 15% of women were employed or looking for jobs; this metric dipped to 9.2% in 2021-22. The best way to improve India’s abysmal ranking is to do it right by women. For that, it is imperative to increase the representation of women in leadership positions at all levels so that women get greater access to jobs and resources. It is up to the Government to move beyond tokenism and help women overcome staggering economic and social barriers.
Q. Choose the antonym of the word 'Abysmal'.
Rearrange the following six sentences a, b, c, d, e and f in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph; then answer the questions given below them.
a) The Supreme Court verdict of May 2014 striking down a statutory provision for prior government clearance for a Central Bureau of Investigation probe against officials of the rank of joint secretary and above is the touchstone against which the constitutionality of the pre-investigation sanction requirement will be tested.
b) The Union government, too, has a set of amendments to the Prevention of Corruption Act pending since 2013, including a proviso for prior sanction.
c) The court had observed that such a provision destroys the objective of anti-corruption legislation, blocks the truth from surfacing, thwarts independent investigation and forewarns corrupt officers.
d) This is the first time a section prescribing punishment for disclosure is being introduced in India, though provisions barring investigation or prosecution without prior sanction are also in force in Maharashtra.
e) Anti-corruption legislation in India seems to be in a state of unacceptable flux.
f) However, the time limit for the sanctioning authority to act is 180 days in Rajasthan, and 90 days in Maharashtra.
Q. Which is the FIFTH sentence of the paragraph?
Three sentences are given. You need to find if they are grammatically correct or incorrect and mark the answer accordingly.
(P) It should be hotter in here if we didn't have an air conditioner.
(Q) He had seen the housekeeper hang the key to the kitchen door on a hook outside
(R) He put on a pair of gloves, took the key, and opened the door.
In the following passage there are blanks, each of which has been numbered. These numbers are printed below the passage and against each five words are suggested, one of which fits the blank appropriately.
The structure of the delta is much ______26_______ that of the Bay of Bengal, but many have dubbed the formation of the delta a fluke of Nature. About two million years___27____, the original route of the Okavango River ended in a lake that is now the salt pans of the Makgadikgadi. Then about 50,000 years ago, a monumental earthquake in Southern Africa _____28_______ a seismic flow disruption for the river, forming the 15,000 square-kilometre wetland ___29___ 11 trillion litres of water. So geologically speaking, the delta is quite young, but has also ______30_______ lifetimes of species thrive and wither.
Find out the appropriate word in each case.
Directions: In the following question, a sentence is given with a highlighted error. Select the option that has the same error as in the given sentence.
Our dog may look fierce but that wouldn’t hurt even a fly.
a. Put you in my position (1)/ and you will realize (2)/ the problems faced in my profession (3)/ No error (4).
b. Vikas sir, being a good teacher (1)/ he is selected (2)/ for the Global Teacher Award (GTA) (3)/ No error (4).
In the following passage there are blanks, each of which has been numbered. These numbers are printed below the passage and against each five words are suggested, one of which fits the blank appropriately.
The structure of the delta is much ______1_______ that of the Bay of Bengal, but many have dubbed the formation of the delta a fluke of Nature. About two million years___2____, the original route of the Okavango River ended in a lake that is now the salt pans of the Makgadikgadi. Then about 50,000 years ago, a monumental earthquake in Southern Africa _____3_______ a seismic flow disruption for the river, forming the 15,000 square-kilometre wetland ___4___ 11 trillion litres of water. So geologically speaking, the delta is quite young, but has also ______5_______ lifetimes of species thrive and wither.
Q. Find out the appropriate word in each case.
Given below is a passage with ten blanks (A-E). A phrase written in brackets is given against each blank. Choose the right word from the options which can replace the phrase most appropriately. If none of the options fit for the replacement, according to you, then select ‘None of these’ as your answer.
Smoke from Australia’s bushfires has travelled far beyond its origins. It crossed New Zealand and South America, and within days had drifted halfway around the globe. NASA predicted the smoke would complete a full _______ (A) (journey or route all the way around) and arrive back where it started. As climate change takes hold and global temperatures rise, bushfires are set to increase in severity and frequency. The _______ (B) (not readily apparent) cause of the fires and resulting smoke haze are often numerous - spanning both natural _______ (C) (tendency to shift or change) and climate change caused by individuals, governments and corporations. Legal and policy frameworks - local, national and international – fail to capture these _______ (D) (scattered about) responsibilities. Despite the _______ (E) (increase in number of something) of climate-related laws in recent decades, bushfire smoke still largely escapes regulation and containment. In this new era of monster fires, our laws need a major rethink.
Q. Which of the following fits the blank labeled (A)?
|
14 docs|63 tests
|