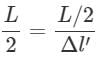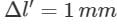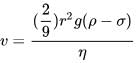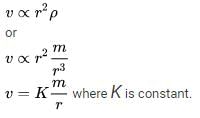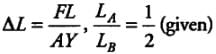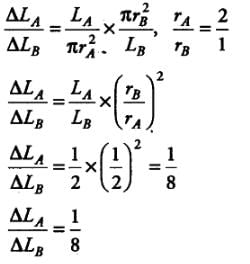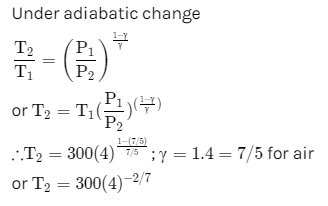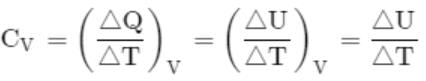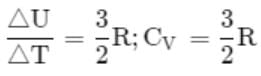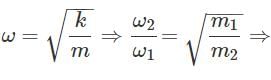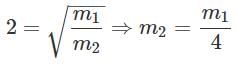NEET Practice Test - 18 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - NEET Practice Test - 18
In the base of an npn transistor, ______ are the minority carriers.
The volume of a cube in m3 is equal to the surface area of the cube in m2. The volume of the cube is:
A ball is released from the top of a tower of height h metres. It takes T seconds to reach the ground. What is the position of the ball in T/3 seconds?
In a uniform circular motion (horizontal) of a ball tied with a string, velocity at any time is at an angle θ with acceleration, then θ is:
Two masses A and B each of mass M are fixed together by a massless spring. A force acts on the mass B as shown in fig. At the instant shown, the mass A has acceleration ‘a’. What is the acceleration of mass B?
Two blocks of masses M1 and M2 are connected with a string passing over a pulley as shown in fig.
The block M1 lies on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the block M1 and the horizontal surface is μ. The system accelerates. What additional mass m should be placed on the block M1 so that the system does not accelerate?
Six marbles are lined up in a straight groove made on a horizontal frictionless surface as shown below. Two similar marbles in contact, with a common velocity v collide with a row of 6 marbles from left. Which of the following is observed?
The power of water pump is 2 kW. If g = 10 m / s2, the amount of water it can raise in 1 minute to a height of 10 m is:
If kinetic energy is doubled, find fractional change in momentum?
When a particle of mass m rotating in a plane circular path of radius r has an angular momentum L. Calculate centripetal force acting on it?
A metre scale is standing vertically on earth’s surface on one of its ends. It now falls on the earth without slipping. Find the velocity with which the free end of the scale strikes the earth g = 9.8 m/s2
The height vertically above the earth’s surface at which the acceleration due to gravity becomes 1% of its value at the surface is (R is the radius of the earth)______.
A particle of mass 10 g is kept on the surface of a uniform sphere of mass 100 kg and radius 10 cm. Find the work to be done against the gravitational force between them to take the particle far away from the sphere [Given G = 6.67 × 10–11Nm2/kg2) ].
For a wire of length l, the maximum change in length under stress condition is 2 mm. What is the change in length under the same conditions when length of wire is halved?
A ball of mass m and radius r is released in viscous liquid. The value of its terminal velocity is proportional to:
The pressure inside two soap bubbles is 1.01 and 1.02 atmosphere respectively. The ratio of their respective volumes is:
A beaker is completely filled with water at 4oC. It will overflow if ______.
Two wires A and B are of the same material. Their lengths are in the ratio 1: 2 and the diameter are in the ratio 2:1. If they are pulled by the same force, then increase in length will be in the ratio:
Find the change in internal energy of the system when a system absorbs 2 kilo-calorie of heat and at the same time does 500 joules of work.
The pressure inside a tyre is 4 times that of the atmosphere. If the tyre bursts suddenly at a temperature of 300 K, what will be the new temperature?
Air is filled at 60°C in a vessel of an open mouth. The vessel is heated to a temperature T so that 1/4th part of the air escapes. Assuming the volume of the vessel remaining constant, the value of T is:
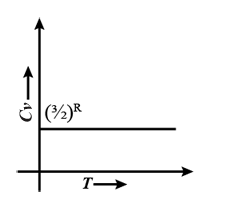
Molar specific heat at constant volume, Cv for a monoatomic gas is:
To make the frequency double of a spring oscillator, we have to:
The displacement-time graph of a particle executing S.H.M. is as shown in Fig.
For the stationary wave,
y = 4 sin (πx / 15) cos (96 πt)
the distance between a node and the next antinode is:
A train is moving at a constant speed along a circular track. The engine of the train emits a sound of frequency n. The frequency heard by the guard at the rear end of the train is:
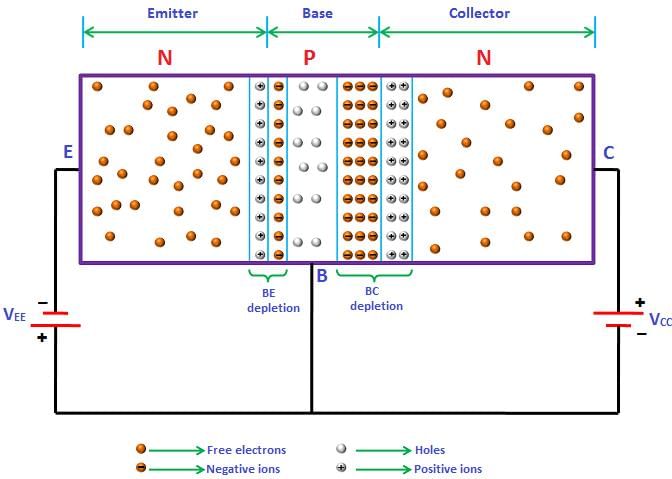
Eight dipoles of charges of magnitude 'e' are placed inside a cube. The total electric flux coming out of the cube will be:
Two condensers, one of capacity C and the other of capacity C/2, are connected to a V volt battery, as shown.
The work done in fully charging both the condensers is:
The resistance between the terminal points A and B of the given infinitely long circuit will be:



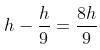
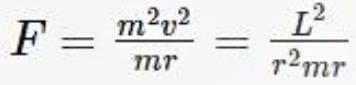
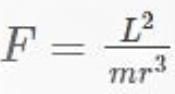
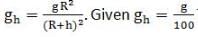
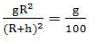
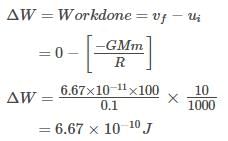

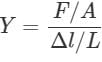
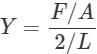 ... (i)
... (i)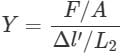 ... (ii)
... (ii)