Olympiad Test: Physical And Chemical Changes - 1 - Class 7 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Olympiad Test: Physical And Chemical Changes - 1
Burning of wood is a ______ change.
What is the main cause of acid rain?
Some pieces of chalk were taken and mixed with water. In this change, how many new substances are formed?
Two changes are stated below
(i) a piece of magnesium gives out bright flames when burnt.
(ii) a piece of iron glows red when heated strongly.
Q. Which of these is a chemical change?
Which of the following changes is not a chemical change?
Which of the following Venn diagrams shows the relationship between changes correctly?
When iron pieces are added to a blue colour copper sulphate solution, the colour of copper sulphate changes to
The gas released when vinegar is mixed with baking soda is
Which of the following is not a physical change?
Manisha took a little bit of soil from her garden and mixed it with water. When she dipped blue litmus in it, the litmus turned red. By adding which of following to her garden will she get better plant growth?
Three substances given below are kept in the open for a few days and some changes were observed.

Which of th e substances will show chemical changes?
Pooja took a candle in a vessel and heated the vessel. Even though the candle did not burn, it changed its shape and state. What kind of change is this?
The product formed when Mg is burnt in air is:
Which of the following is an antacid?
Adding sodium chloride to water is a
Three different substances were taken and tested with litmus paper. The results are given below. 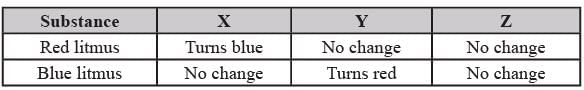
What could be the substance X?
Three different substances were taken and tested with litmus paper. The results are given below.

What could be the substance Y?



















