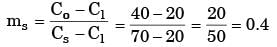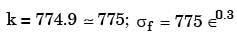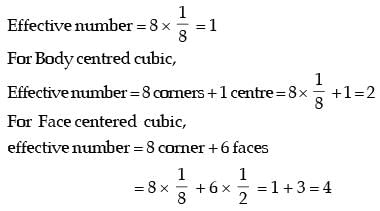Past Year Questions: Engineering Materials - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Past Year Questions: Engineering Materials
When 1.0% plane carbon steel is slowly cooled from the molten state to 740°C, the resulting structure will contain
[1990]
During heat treatment of steel, the hardness of various structures in increasing order is
[ME 2003]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Cold working of steel is defined as working
[ME 2003]
Hardness of steel greatly improves with
[ME 2003]
From the lists given below, choose the most appropriate set of heat treatment process and the corresponding process characteristies
Process
P. Tempering
Q. Austempering
R. Martempering
Characteristics
1. Austenite is converted into bainite
2. Austenite is converted into martensite
3. Cementite is converted into globular structure
4. Both hardness and brittleness are reduced
5. Carbon is absorbed into the metal
[ME 2004]
When the temperature of a solid metal increases,
[ME 2005]
The main purpose of spheroidising treatment is to improve
[ME 2006]
Match the items in columns I and II.
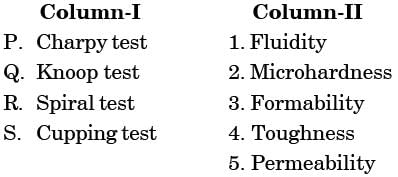
[ME 2006]
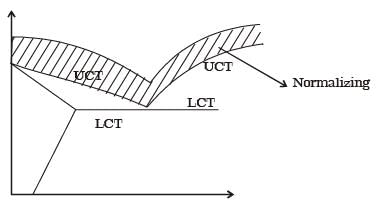
During normalizing process of steel, the specimen is heated
[ME 2012]
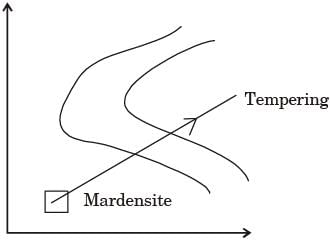
The process of reheating the martensitic steel to reduce its brittleness without any significant loss in its hardness is
[ME 2014, Set-1]
Match the heat treatment processes (Group A) and their associated effects on properties (Group B) of medium carbon steel

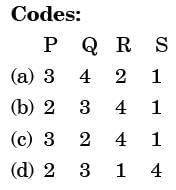
[ME 2014, Set-4]
Increase in carbon content in plain carbon steel raise its
[PI 1992]
The iron carbon diagram and the TTT curves are determined under
[ME 1996]
The percentage of carbon in grey cast iron is in the range of
[ME 2004]
If a particular Fe-C alloy contains less than 0.83% carbon, it is called
[ME 2007]
In a binary system of A and B a liquid of 20% A (80% B) is coexisting with a solid of 70% A(30%B). For an overall composition having 40% A the fraction of solid is
[ME 2016, Set-2]
In the phase diagram shown in the figure, four samples of the same composition are heated to temperatures marked by a, b, c and d.
Composition (Arbitrary Units)
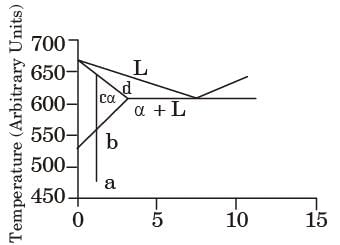
At which temperature will a sample get solutionized the fastest?
[ME 2016, Set-2]
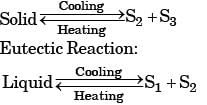
Denoting L as liquid and M as solid in a phasediagram with the subscripts representing different phases, a eutectoid reaction is described by
[ME 2018, Set-2]
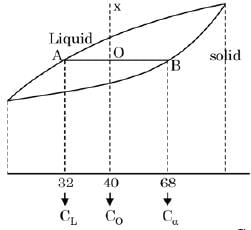
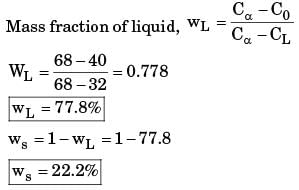
The binary phase diagram of metals P and Q is shown in the figure. An alloy X containing 60% P and 40% Q (by weight) is cooled from liquid to solid state. The fractions of solid and liquid (in weight percent) at 1250°C, respectively, will be
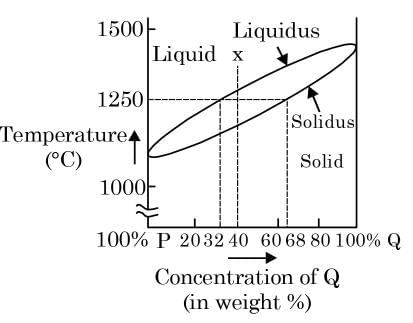
[ME 2019, Set-2]
The ultimate tensile strength of a material is 400 MPa and the elongation up to maximum load is 35%. If the material obeys power law of hardening, then the true stress-true strain relation (stress in MPa) in the plastic deformation range is
[ME 2006]
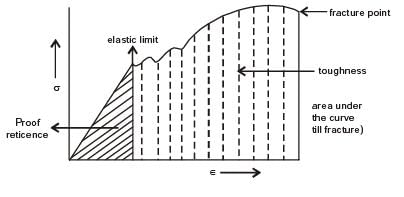
For a ductile material, toughness is a measure of
[ME 2013]
The "Jominy test" is used to find
[ME 2016, Set-1]
Hardenability of steel is a measure of
[ME 2019,Set-2]
The most widely used reinforcement in modern day FRP tennis racket is
[PI 1992]
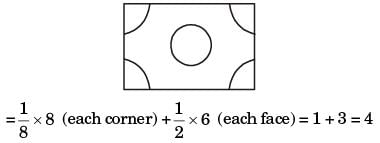
The effective number of lattice points in the unit cell of simple cubic, body centered cubic, and face centered cubic space lattices, respectively, are
[ME 2009]
Which of the following is the correct data structure for solid models?
[ME 2009]
The material property which depends only on the basic crystal structure is
[ME 2010]
The crystal structure of austenite is
[ME 2011]
The crystal structure of aluminium is
[ME 2017, Set-2]
The number of atoms per unit cell and the number of slip systems, respectively, for a facecentered cubic (FCC) crystal are
[ME 2018, Set-1]