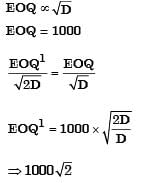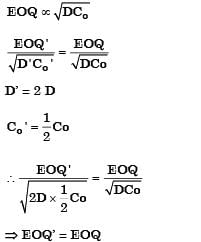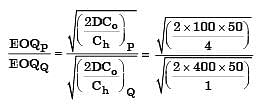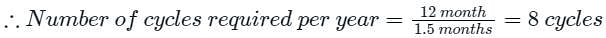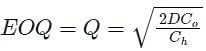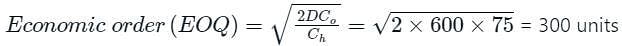Past Year Questions: Inventory Control - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Past Year Questions: Inventory Control
One of the following statements about PRS (Periodic Reordering System) is not true identify.
[1998]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In an ideal inventory control system, the economic lot size for a part is 1000. If the annual demand for the part is doubled, the new economic lot size required will be
[1989]
When the annual demand of a product is 24000 units, the EOQ (Economic Order Quantity) is 2000 units. If the annual demand is 48000 units the most appropriate EOQ will be
[1991]
If the demand for an item is doubled and the ordering cost halved, the economic order quantity
[1995]
In inventory planning, extra in ventory is unnecessarily carried to the end of the planning period when using one of the following lot size decision policies:
[1998]
In computing Wilson's economic lot size for an item, by mistake the demand rate estimate used was 40% higher than the true demand rate. Due to this error in the lot size computation, the total cost of setup plus inventory holding per unit time. Would rise above the true optimum by approximately
[1999]
Market demand for springs is 8,00,000 per annum.A company purchases these spring in lots and sells them. The cost of making a purchase order is Rs. 1,200. The cost of Storage of springs is Rs. 120 per stored piece per annum. The economic order quantity is
[2003]
There are two products P and Q with the following characteristics
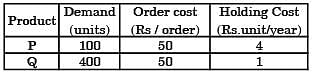
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) of products P and Q will be in the ratio?
[2004]
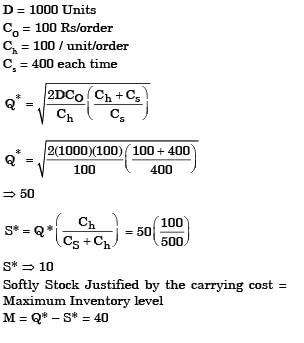
A company has an annual demand of 1000 units, ordering cost of Rs. 100/ order and carrying cost of Rs. 100/unit-year. If the stockout costs are estimated to be nearly Rs. 400 each time the company runs out-of-stock, the safety stock justified by the carrying cost will be
[2004]
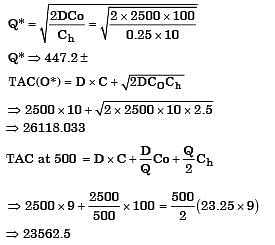
Consider the following data for an item. Annual demand : 2500 units per year Ordering cost: Rs. 100 per order, Inventory holding rate: 25% of unit price Price quoted by a supplierThe optimum order quantity (in units) is
[2006]
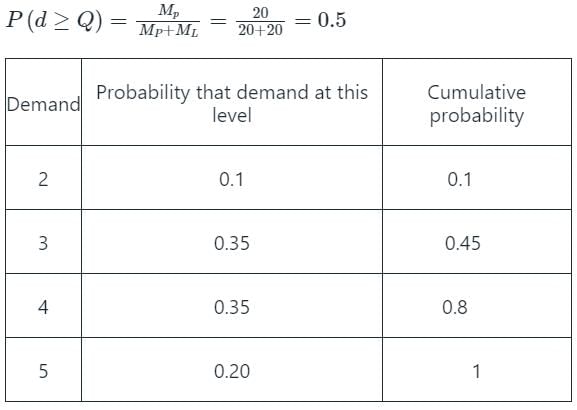
A stockist wishes to optimize the number of perishable items he needs to stock in any month in his store. The demand distribution for this perishable item is
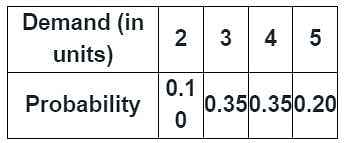
The stockist pays Rs. 70 for each item and he sells each at Rs. 90. If the stock is left unsold in any month, he can sell the item at Rs. 50 each. There is no penalty for unfulfilled demand. To maximize the expected profit, the optimal stock level is
[2006]
The maximum level of inventory of an item is 100 and it is achieved with infinite replenishment rate. The inventory becomes zero over one and half month due to consumption at a uniform rate. This cycle continues through out the year. Ordering cost is Rs. 100 per order and inventory carrying cost is Rs. 10 per item per month. Annual cost (in Rs.) of the plan, neglecting material cost, is
[2007 : 2 Marks]
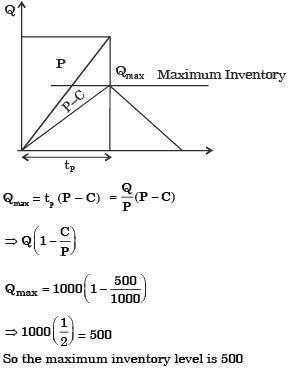
In machine shop, pins of 15 mm diameter are produced at a rate of 1000 per month and the same is consumed at a rate of 500 per month.The production and consumption continue simultaneously till the maximum inventory is reached. Then inventory is allowed to reduce to zero due to consumption. The lot size of production is 1000. If backlog is not allowed, the maximum inventory level is
[2007]
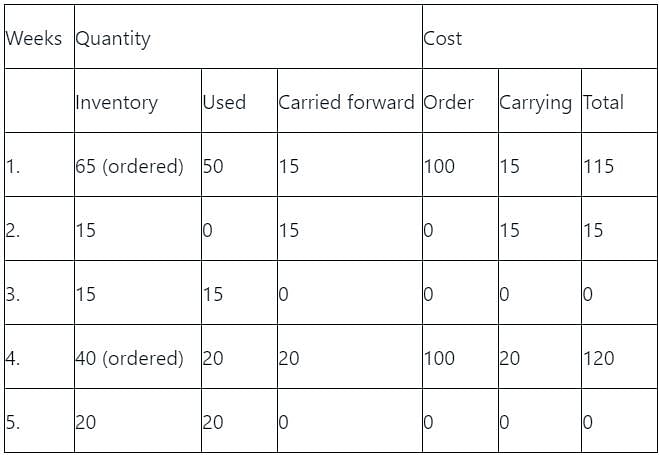
The net requirements of an item over 5 consecutive weeks are 50-0-15-20-20. The inventory carrying cost and ordering cost are Rs. 1 per item per week and Rs. 100 per order respectively. Starting inventory is zero. Use "Least Unit Cost Technique" for developing the plan. The cost of the plan (in Rs.) is
[2007]
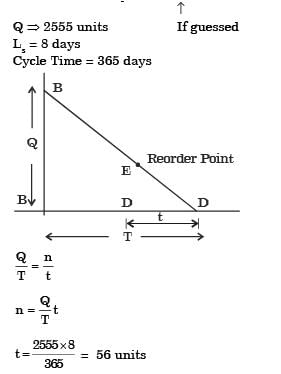
A company uses 2555 units of an item annually.Delivery lead time is 8 days. The reorder point (in number of units) to achieve optimum inventory is
[2009]
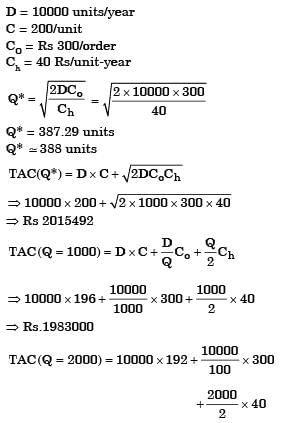
Annual demand for window frames is 10000.Each frame costs Rs. 200 and ordering cost is Rs. 300 per order. Inventory holding cost is Rs. 40 per frame per year. The supplier is willing to offer 2% discount if the order quantity is 1000 or more, and 4% if order quantity is 2000 or more. If the total cost is to be minimized, the retailer should
[2010]
A component can be produced by any of the four processes I, II, III and IV. The fixed cost and the variable cost for each of the processes are listed below. The most economical process for producing a batch of 100 pieces is
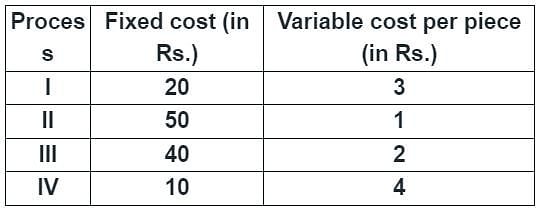
[2014]
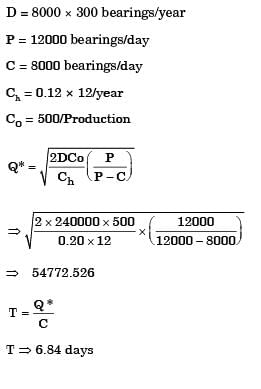
A manufacturer can produce 12000 bearings per day. The manufacturer received an order of 8000 bearings per day from a customer. The cost of holding a bearing in stock is Rs. 0.20 per month. Setup cost per production run is Rs. 500. Assuming 300 working days in a year, the frequency of production run should be
[2014]
A local tyre distributor expects to sell approximately 9600 steel belted radial tyres next year. Annual carrying cost is Rs. 16 per tyre and ordering cost is Rs. 75. The economic order quantity of the tyres is
[2018]