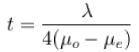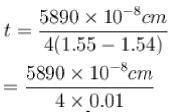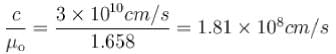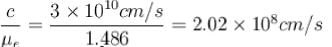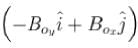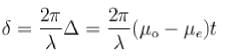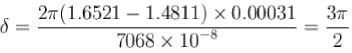Polarization MCQ - Physics MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Polarization MCQ
When ordinary light is passed through rotating crystal, there is no variation in the intensity of the emergent light, this implies that
Find the thickness of a quater-wave plate when the wavelength of light is equal to 5890 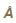 and μo = 1.55 μe = 1.54.
and μo = 1.55 μe = 1.54.
The thickness of a quater-wave plate for which μo > μe (such as calcite) is given by
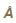 and μo = 1.55 μe = 1.54.
and μo = 1.55 μe = 1.54.The thickness of a quater-wave plate for which μo > μe (such as calcite) is given by
For calcite, nO = 1.65836, ne = 1.48641 at 18°C and for λ = 5893  . The thickness of the quarter wave plate is :
. The thickness of the quarter wave plate is :
 . The thickness of the quarter wave plate is :
. The thickness of the quarter wave plate is :Calculate the velocities of extraordinary rays in calcite crystal in a plane perpendicular to the optic axis. Given μO = 1.658, μe = 1.486 and c = 3 x 1010 cm/s.
If the plane wave is split & recombined on a screen after the two portions, which are polarized in the x & y directions, have travelled an optical path difference of 2π/k the observed average intensity will be proportional to :
Consider a plane wave that propagates through empty space 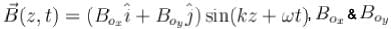 are positive constants. What can you say about the polarization of this wave :
are positive constants. What can you say about the polarization of this wave :
When scattered blue light is seen through a rotating nicol prism, a variation of intensity with zero minimum intensity is seen. What does this imply?
Let dw be the work done in a quasistatic reversible thermodynamic process.
Which of the following statements about dw is correct?
A calcite plate 0.0031 mm thick is cut and polished such that its optic axis is parallel to the surface. A plane polarized white light from a polariser is incident normally on the plate. Estimate the phase difference if the emergent beam for wavelengths is 7068 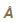 , and μO = 1.6521 μe = 1.4811.
, and μO = 1.6521 μe = 1.4811.
The velocity of light in water is 2.2 X 108 m/s. What is the polarizing angle of incidence?