Psychology: CUET Mock Test - 2 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Psychology: CUET Mock Test - 2
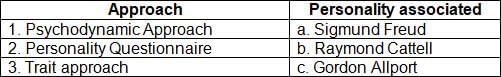
Which of the following best describes the trait approach to the study of personality?
Which of the following approaches was developed in response to the post-Freudian approaches to studying personality?
Behavioural Analysis to assess personality contains data obtained from which of the following tests?
1. Interview
2. Nomination
3. Observation
4. Ratings
Choose the correct answer using the codes given below:
2. Nomination
3. Observation
4. Ratings
Consider the following statements:
- Personal self leads to an orientation in which one feels primarily concerned with oneself.
- The personal self emerges in relation with others.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
- In repression, anxiety-provoking behaviours or thoughts are totally dismissed by the unconscious.
- In projection, people attribute their own traits to others.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to the Behavioural approach, consider the following statements:
- This approach has given importance to the internal dynamics of behaviour.
- It focuses on learning stimulus-response connections and their reinforcement.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
_______ states that the presence of two mutually-opposing forces at the same time inhibits the weaker force.
The past is relevant only to the extent of understanding the origins of the faulty behaviour and thought patterns. Which therapy propagates this view?
In _______ , the aim is to establish a relationship between undesirable behaviour with painful consequences.
Learning by observing others is used through a process of rewarding small changes in the behaviour, the client gradually learns to acquire the behaviour of the model. This is called:
Which of the following does NOT contribute towards Ethical Standards in psychotherapy?
Praising the child when he eats properly is an example of:
Research suggests that we seek out the company of others because of which motives?
Which of the following factors facilitate group formation ?
Social facilitation refers to an increase in dominant responses in the presence of others of the same species, leading to:
Which one of the following statements about social support is true?
According to research by Latane and Darley, why did witnesses fail to intervene and help Kitty Genovese before she was murdered?
A person consistently feels sad when they hear about environmental damage but does nothing to stop it. This represents:
What is the term for attitudes that influence a person’s self-concept or view of themselves?
The main aim of attitude change in advertising is to:
________ is removing the evil that resides in the individual through counter magic and prayer.
"I should be loved by everyone at all times ", "I must be liked by all." This thought/belief can be treated using which therapy?
Who defined stress as “the nonspecific response of the body to any demand”?
Frustration is one of the sources of ________ stress.