QUIZ 2:Radioactivity And Nuclear Physics(#freetestseries) - JEE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - QUIZ 2:Radioactivity And Nuclear Physics(#freetestseries)
The graph between wave number (ν¯) and angular frequency (w) is [AIIMS 2002]
Binding energy per nucleon plot against the mass number for stable nuclei is shown in the figure. Which curve is correct [Orissa JEE 2002] 

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Binding energy per nucleon verses mass number curve for nuclei is shown in the figure. W, X, Y and Z are four nuclei indicated on the curve. The process that would release energy is [IIT-JEE 1999] 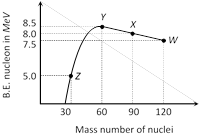

The graph between the instantaneous concentration (N) of a radioactive element and time (t) is
The count rate of 10g of radioactive material was measured at different times and this has been shown in the figure. The half-life of material and the total counts (approximately) in the first half life period, respectively are [CPMT 1986] 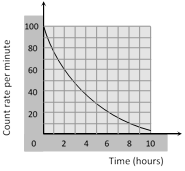
A radioactive material decays b simultaneous emission of two particles with respective half-lives 1620 and 810 years. The time, in years, after which one-fourth of the material remains is ?
A nucleus at rest breaks into two nuclear parts which have their velocities ratio equal to 8: 1. The ratio of their nuclear radii is .....
Ten grams of 57Co kept in an open container beta-decays with a half-life of 270 days. The weight of the material inside the container after 540 days will be nearly (in grams)?
the half-life of 24Na is 15.0 h. How long does it take for 80 percent of a sample of this nuclide to decay? [In 5=1.6](in h)
Tritium (31H) has a half-life of 12.5y against beta decay. What fraction of a sample of tritium will remain undecayed after 25y?
Assertion : Neutrons penetrate matter more readily as compared to protons. Reason : Neutrons are slightly more massive than protons. [AIIMS 2003]
Assertion : Radioactive nuclei emit β−1 particles. Reason : Electrons exist inside the nucleus. [AIIMS 2003]
Assertion : Density of all the nuclei is same. Reason : Radius of nucleus is directly proportional to the cube root of mass number. [AIIMS 2000]
Assertion : Isobars are the element having same mass number but different atomic number. Reason : Neutrons and protons are present inside nucleus. [AIIMS 1997]
Assertion : The ionising power of b-particle is less compared to a-particles but their penetrating power is more. Reason : The mass of b-particle is less than the mass of a-particle.

















