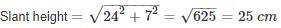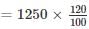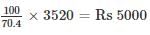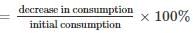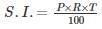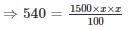Practice Test: Quantitative Aptitude - 8 - SSC CGL MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Practice Test: Quantitative Aptitude - 8
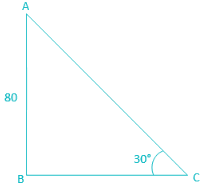
A kite is flying at a height of 80 m from the level ground, attached to a string inclined at 30° to the horizontal. The length of the string is?
If tan θ + cot θ = 2, then the value of tannθ + cotnθ (0° < θ < 90°, n is an integer) is
Find the coefficient of x2 in the expansion of (x2 + x + 1) (x2 – x + 1)
Directions: Study the following Histogram and answer the following questions.
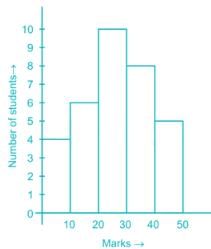
Q. The ratio of the students obtaining marks in the first and the last interval is
Directions: Study the following Histogram and answer the following questions.
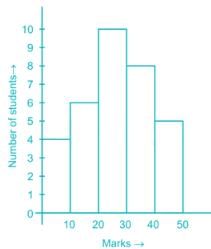
Q. The least number of students got the marks in the interval
Directions: Study the following Histogram and answer the following questions.
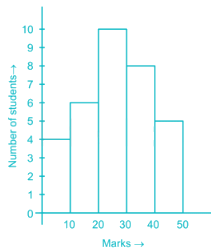
Q. The maximum number of students got the marks in the interval of
Directions: Study the following Histogram and answer the following questions.

Q. The total number of students involved in the data is
The intersecting point of the graphs x – y = 0 and x + y – 4 = 0 is
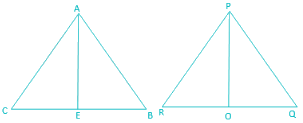
If sides AB, BC and the median AE in ΔABC is similar to the sides PQ, QR and median PO in ΔPQR. State whether ΔABC is similar to, ΔPQR?
If AD is the median of the triangle ABC and G be the centroid, then the ratio of AG:AD is
Let the lengths of the sides of a triangles be represented by x + 3, 2x – 3 and 3x – 5. If the perimeter of the triangle is 31, then the length of the longest side is
At each corner of a triangular field of sides 26 m, 28 m and 30 m, a cow is tethered by a rope of, length 7 m. The area (in m2) ungrazed by the cows is
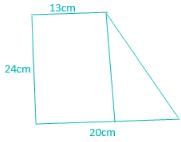
The radii of the two ends of a frustum are 20 cm and 13 cm respectively. If the height of the frustum is 24 cm, then its slant height is
Raman takes twice time as much as Ajay to do a work. If they work together, the work is completed in 12 days. How many days will Raman take to complete the work alone?
A bus rides at the rate of 48 kms/hr and stops for 18 mins to change course after every 18kms. Total time taken by him to cover a distance of 288 km is –
Mayur is walking at a speed of 15 km per hour. After every km, he takes rest for 6 minutes. How much time will he take to cover a distance of 11 km?
A fruit seller purchased 50 kg of mangoes at the rate of Rs. 25 per kilo. He sold some of the mangoes at the rate of Rs. 40 per kilo and the rest at the rate of Rs. 15 per kilo. If he incurred 20% profit overall, the amount of mangoes sold at the rate of Rs. 15 per kilo is
A shopkeeper gives 12% additional discount on the discounted price after giving an initial discount of 20 % on the labeled price of a radio. If the final sale price is Rs. 3520, then what is its labeled price?
The average age of the boys in a class of 20 boys is 15.6 years. What will be the average age if 5 new boys come whose average is 15.4 years?
The price of a commodity rises from Rs. 6 per kg to Rs. 7.50 per kg. If the expenditure cannot increase, the percentage of reduction in consumption is
Neena borrows Rs. 1500. The rate of simple interest is same as the number of years the money has been borrowed for. If she gives Rs. 540 as interest at the end of the stipulated period, the rate of interest p.c.p.a. will be
An alloy contains copper, zinc and nickel in the ratio of 5:3:2. The quantity of nickel in kg that must be added to 100 kg of this alloy to have the new ratio 5:3:3 is
Four identical circles of radius 4 cm each touch each other externally. The area of the region bounded by the four circles (in cm2) is
From each corner of a square of side 4 cm, a quadrant of a circle of radius 1 cm is cut and also a circle of diameter 2 cm is cut as shown is figure. The area of the remaining (shaded) portion is


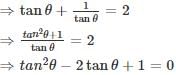


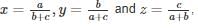 then value of xy + yz + zx + 2xyz is
then value of xy + yz + zx + 2xyz is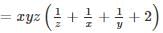
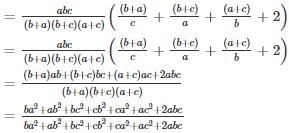
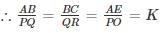
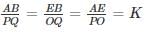

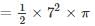
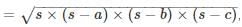 where s is the semi perimeter of the triangle
where s is the semi perimeter of the triangle