Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Tests > Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Class 10 MCQ
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Class 10 MCQ
Test Description
26 Questions MCQ Test - Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science for Class 10 2024 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Class 10 exam syllabus.The Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science MCQs are made for Class 10 2024 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science below.
Solutions of Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science questions in English are available as part of our course for Class 10 & Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science solutions in
Hindi for Class 10 course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science | 26 questions in 52 minutes | Mock test for Class 10 preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Class 10 Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 1
Light is a form of energy produced by a ______.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 1
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 2
An example for non-luminous object is ___________.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 3
The phenomenon by which the incident light falling on a surface is sent back into the same medium is known as ________.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 3
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 4
When light is incident on a polished surface ___________ reflection takes place.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 4
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 5
An object becomes invisible when it undergoes ______ reflection.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 5
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 6
The image formed by a plane mirror is always _______.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 6
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 7
The centre of the sphere of which the spherical mirror forms a part is called ____________.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 7
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 8
The focus of a concave mirror is ________.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 8
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 9
A converging mirror is known as ________.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 9
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 10
An image formed by a convex mirror is always ________.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 10
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 11
If the image formed by a concave mirror is virtual, erect and magnified, then the object is placed __________.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 11
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 12
Dentists use a _____________ to focus light on the tooth of a patient.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 12
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 13
An object placed 2m from a plane mirror is shifted by 0.5 m away from the mirror. What is the distance between the object and its image?
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 13
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 14
What is the value of q in the following diagram?
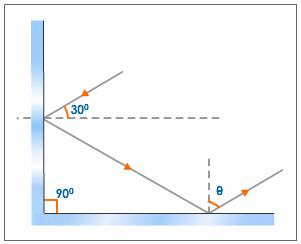
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 15
What is the angle between the incident and reflected rays when a ray of light is incident normally on a plane mirror?
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 15
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 16
Name the type of image that can be obtained on a screen.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 16
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 17
A ray of light is incident on a plane mirror and the angle of reflection is 50 degree. Calculate the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 17
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 18
Which of the following is used to make a periscope?
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 18
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 19
Which mirror has a wider field of view?
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 19
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 20
The focal length of a concave mirror is 15 cm. What is its radius of curvature?
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 20
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 21
The focal length of a mirror is 15 cm. Identify the type of mirror.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 21
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 22
A ray of light passing through the _______ retraces its path.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 22
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 23
When an object is placed at the focus of a concave mirror, the image will be formed at ________.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 23
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 24
Butter paper is an example for _______ object.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 24
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 25
An object of size 2.0 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave mirror. The distance of the object from the mirror equals to the radius of curvature. The size of the image will be ______________.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 25
Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 26
If an incident ray passes through the centre of curvature of a spherical mirror, the reflected ray will __________________.
Detailed Solution for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science - Question 26
Information about Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Reflection Of Light - Practice Test, Class 10 Science, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF

















