Revisal Problems (Past 13 Year) JEE Advanced (Alkyl Halides) - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Revisal Problems (Past 13 Year) JEE Advanced (Alkyl Halides)
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-12) This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (cj and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
What is the major product of the reaction?
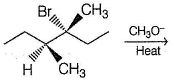
What is the major elimination product of the following reaction?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following is missing reagent in the following reaction sequence?
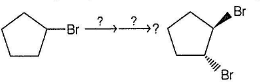
Predict substitution product in the following reaction.
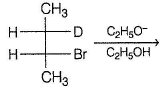
Propose product with a ppropriate stereochemistry in the following SN2 reaction.
In SN1 reaction, racemisation occurs if the reaction occurs at a ste reogenic centre, however 50 : 50 mixture of enantiomers are rarely obtained, why?
Arrange the following halides in decreasing order of reactivity in SN1 reaction.
Arrange the following compounds in decreasing order of reactivity for hydrolysis reaction.
I. PhCH2Br
The in creasing order of reactivity of the following bromides in SN1 reaction is
Which is the least reactive in solvolysis reaction?
Among the following given bromides, the correct decreasing order of reactivity in SN1 reaction is
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their rate hydrolysis by SN1 mechanism.
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-22) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
What are the expected products of the following reaction?
What is (are) true about E1cb reaction?
Which of the following is expected to give more than two products in an E2 elimination reaction?
Consider the following elimination reaction,
Q.
The statement that is (are) true regarding the above elimination reaction is
Consider the following reactions:
Q.
The correct statement regarding above substitution reaction is/are
Which of the following will result in racemic mixture as major solvolysis products?
Consider the following solvolysis reaction.
Q.
The expected product(s) is
Select the correct statement.
Consider the follow ing SN2 reaction,
What is (are) true about the following free radical chlorination reaction ?
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 23-25) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc.
Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
Compounds A, B and C are alkyl bromides with the molecular formulate C5H11Br. Treatment of A or B with potassium ferf-butoxide gives the same alkene D. If the base is changed to sodium ethoxide, A and C give the same alkene E. Treatment of C with potassium ferf-butoxide gives yet another alkene F.
Q.
The correct statement regarding A, B and C is
Compounds A, B and C are alkyl bromides with the molecular formulate C5H11Br. Treatment of A or B with potassium ferf-butoxide gives the same alkene D. If the base is changed to sodium ethoxide, A and C give the same alkene E. Treatment of C with potassium ferf-butoxide gives yet another alkene F.
Q.
The correct statement concerning A, B and C is
Compounds A, B and C are alkyl bromides with the molecular formulate C5H11Br. Treatment of A or B with potassium ferf-butoxide gives the same alkene D. If the base is changed to sodium ethoxide, A and C give the same alkene E. Treatment of C with potassium ferf-butoxide gives yet another alkene F.
Q.
Which forms most stable Grignard’s reagent when treated with Mg in THF?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 26-29) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
Methyl cyclopentane on treatment with chlorine gas in sunlight undergo free radical chlorination reaction. How many of the above monochlorination products upon treatment with ethanolic KOH solution can give 1-methyl cyclopentane as one of the product?
In principle, how many different alkyl chlorides would be formed on treatment of 3-methyl-2-pentanol with concentrated HCI in the presence of ZnCI2?
How many different isomers of alkyl bromide on treatment with ethanolic KOH solution can result in 3-methyl-3-hexene?
If Br2CH—CHBr2 is treated with excess of NaCN solution such that all bromides are substituted by nucleophiles, how many different substitution products would be formed in principle which are chiral?
Matching List Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 30 and 31) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.
Q.
Match the reactions from Column I and their corresponding properties from Column II and mark the correct option from codes given below.

















