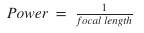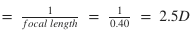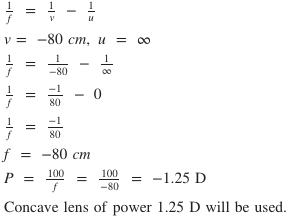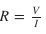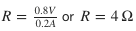SA I - Full Physics Test 2 - Class 10 MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - SA I - Full Physics Test 2
A convex lens has a focal length of 40 cm. Calculate its power.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Match the following with correct response.
(1) Amrita Devi Bishnoi
(2) Sunder Lal Bhaguna
(3) A.K. Banerjee
(4) Pandurang Hegde
(A) Appiko movement
(B) Leader of chipko movement
(C) Protecting khejri trees
(D) Forest officer who rejuvenate degraded forest
(1) Amrita Devi Bishnoi
(2) Sunder Lal Bhaguna
(3) A.K. Banerjee
(4) Pandurang Hegde
(A) Appiko movement
(B) Leader of chipko movement
(C) Protecting khejri trees
(D) Forest officer who rejuvenate degraded forest
The magnetic field at a point due to current carrying conductor is directly proportional to
A. Current flowing through the conductor
B. Distance of the conductor
C. Resistance of the conductor
D. None of the above
Match the following with correct response.
(1) Power of accommodation
(2) Near point
(3) Far point
(4) Least distance of distinct vision
(A) Farthest point to which the eye see clearly
(B) The ability of eye lens to focus near and far objects
(C) Generally increases with age
(D) Nearest point which the eye can see clearly
Match the following with correct response.
(1) Cataract
(2) Myopia
(3) Hyper metropia
(4) Presbyopia
(A) Old age person unable to see near objects clearly due to weakening of ciliary muscles
(B) A person can see near objects but not able to see for objects clearly
(C) Opacity of the lens
(D) A person can see far objects but not able to see near objects clearly
The far point of a myopic person is 80cm in front of the eye. Which type of lens is required to correct the problem?
The function of rheostat in an electrical circuit is to:
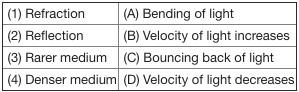
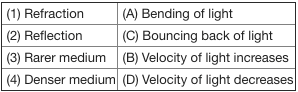
Match the following with correct response.
(1) Atmospheric refraction
(2) Scattering of light
(3) Dispersion
(4) Tyndall effect
(A) Twinkling of star
(B) Rainbow
(C) Red colour of rising sun
(D) White colour of clouds
In an electric circuit, the direction of electric current is:
Match the following with correct response.
(1) Michael Faraday
(2) Fleming
(3) Maxwell
(4) H.C. Oersted
(A) Direction of magnetic lines of force due to straight conductor
(B) Electromagnetic induction
(C) Electromagnetism
(D) Direction of force experienced by a current conductor placed in magnetic
Match the following with correct response.
(1) Colour code of earth wire
(2) Dry cell
(3) A coil wound into a tightly packed helix
(4) Magnets that have temporary magnetism
(A) Electromagnet
(B) Direct current
(C) Green
(D) Solenoid
Match the following with correct response.
(1) Appliances with exposed metal parts always need
(2) The unidirectional current flow in the circuit
(3) The current which changes its direction at regular intervals
(4) Device that makes use of the fact that magnetism in presence of electricity produces motion
(A) D.C
(B) Electric motor
(C) A.C
(D) Three pin plug
Match the following with correct response.
(1) The group of solar cells joined together in definite pattern
(2) The device used for obtaining energy for flowing water
(3) A barrier constructed on the river to store the flowing water
(4) A domestic fuel which contains butane
(A) Dam
(B) Solar panel
(C) LPG
(D) Water wheel
The lateral displacement of an incident ray passing out of a rectangular glass slab
Match the following with correct response.
(1) Nuclear energy
(2) Geothermal energy
(3) Fission
(4) Nuclear fusion
(A) Two light weight nuclei combine to from a big nuclei
(B) energy present inside the earth's crust
(C) Energy obtained from the nucleus of an atom
(D) Breaking of heavy nucleus into two medium sized nuclei
Which of the following is the source of air pollution?
When light enters from air to glass, which of the following changes:
A. Wavelength
B. Velocity
C. Frequency
D. Amplitude
Name the process through which oxygen was added to the atmosphere
LPG is better fuel than kerosene because-
A. LPG has low calorific value
B. LPG does not Produce smoke
C. LPG does not leave any ash
D. It has high ignition temperature
Ammeter is likely to burn out if you connect it in parallel because:
The nature of image formed by a mirror is not affected by the position of the object. The mirror is:
Calculate the resistance of a conductor if the current flowing through it is 0.2 A, when potential difference applied is 0.8 V.