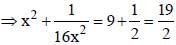SSC CGL Previous Year Questions: Algebra- 5 - SSC CGL MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test SSC CGL Previous Year Papers - SSC CGL Previous Year Questions: Algebra- 5
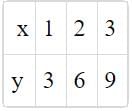
The linear equation such that each point on its graph has an ordinate four times its abscissa is: (SSC Sub. Ins. 2013)
If x = a – b, y = b – c, z = c – a, then the numerical value of the algebraic expression x3 + y3 + z3 – 3xyz will be (SSC Sub. Ins. 2013)
If xy + yz + zx = 0, then 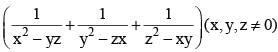 is equal to (SSC CHSL 2013)
is equal to (SSC CHSL 2013)
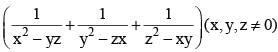 is equal to (SSC CHSL 2013)
is equal to (SSC CHSL 2013)If 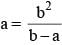 then the value of a3 +b3 is (SSC CHSL 2013)
then the value of a3 +b3 is (SSC CHSL 2013)
Let 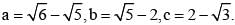 Then point out the correct alternative among the four alternatives given below. (SSC CHSL 2013)
Then point out the correct alternative among the four alternatives given below. (SSC CHSL 2013)
If a2 + b2 + c2 = 2 (a – b – c) – 3, then the value of 2a – 3b + 4c is (SSC CHSL 2013)
If 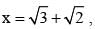 then the value of x3 - (1/x3) is: (SSC CHSL 2012)
then the value of x3 - (1/x3) is: (SSC CHSL 2012)
If the difference of two numbers is 3 and the difference of their squares is 39; then the larger number is : (SSC CHSL 2012)
If 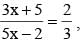 then the value of x is : (SSC CHSL 2012)
then the value of x is : (SSC CHSL 2012)
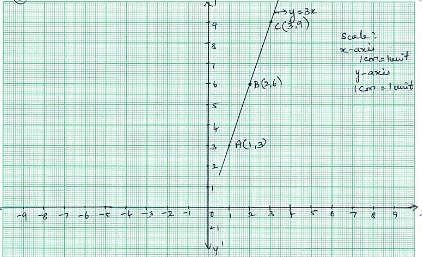
The equation of this graph is (SSC Sub. Ins. 2012)
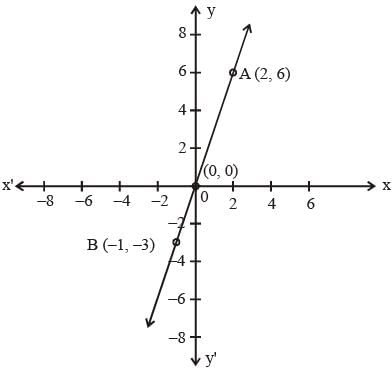
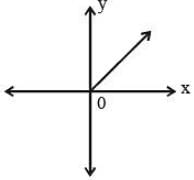
The graph of y = x + | x | is given by (SSC Sub. Ins. 2012)
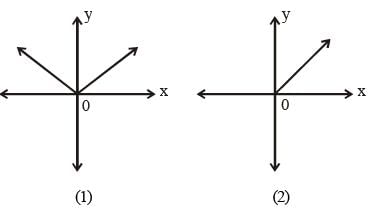
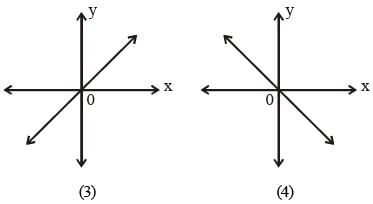
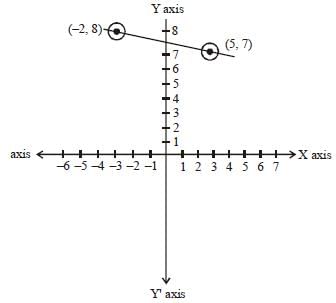
The line passing through the points (– 2, 8) and (5, 7) (SSC Sub. Ins. 2012)
If (3x – y) : (x + 5y) = 5 : 7, then the value of (x + y) : (x – y) is (SSC Sub. Ins. 2012)
If a + b = 5, a2 + b2 = 13, the value of a – b (where a > b) is (SSC Sub. Ins. 2012)
Minimum value of 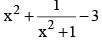 is (SSC Sub. Ins. 2012)
is (SSC Sub. Ins. 2012)
If 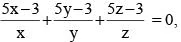 then the value of
then the value of 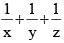 is (SSC Sub. Ins. 2012)
is (SSC Sub. Ins. 2012)
If a, b, c are real and a3 + b3 + c3 = 3abc and a +b +c ≠ 0, then the relation between a, b, c will be (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
If a +b +c= 0 , the value of 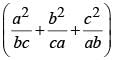 is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
If x = 3+ 2√2, then the value of 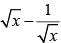 is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
If 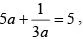 then the value of
then the value of 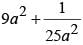 is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
If 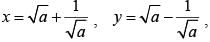 then the value of x4 + y4 – 2x2y2 is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
then the value of x4 + y4 – 2x2y2 is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
If a + b + c = 8, then the value of (a – 4)3 + (b – 3)3 + (c – 1)3 – 3 (a – 4) (b – 3) (c – 1) is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
The area (in sq. unit) of the triangle formed by the three graphs of the equations x = 4, y = 3, and 3x + 4y = 12, is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
If x = 997, y = 998, z = 999, then the value of x2 + y2 + z2 – xy – yz – zx will be (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
If x = (4ab/a+b), then the value of 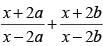 is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2012)
The area of the triangle formed by the lines 5x + 7y = 35, 4x + 3y = 12 and x-axis is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
If 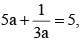 the value of
the value of 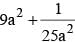 is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
If 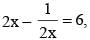 then the value of
then the value of 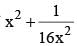 is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
If a2 + b2 + c2 = 2(a – b – c) – 3 then the value of 2a – 3b + 4c is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2012)
|
319 docs|337 tests
|



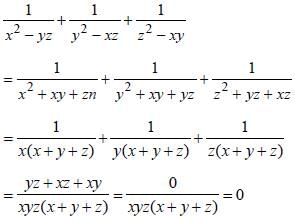
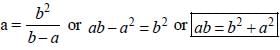
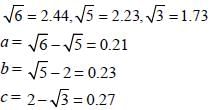
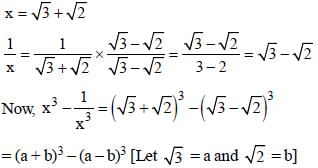
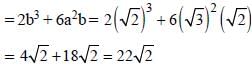
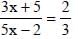
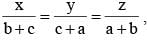 then : (SSC CHSL 2012)
then : (SSC CHSL 2012)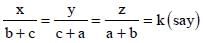
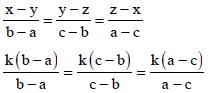
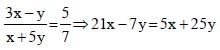
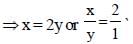 ...(1)
...(1)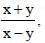 Divide numerator & denominator by y.
Divide numerator & denominator by y.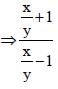
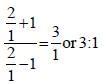
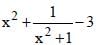
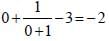
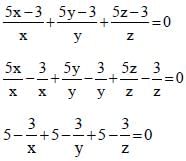
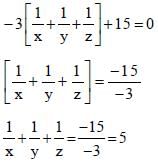
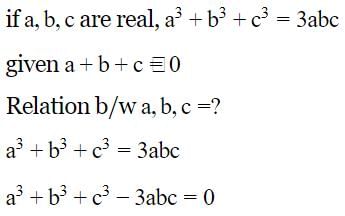
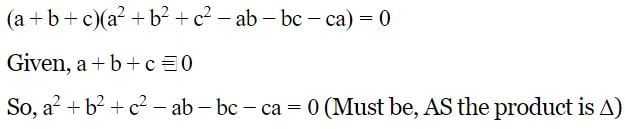
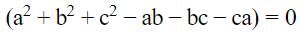
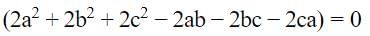
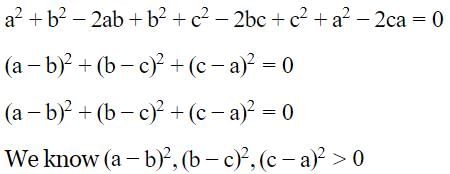
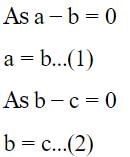
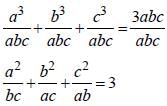
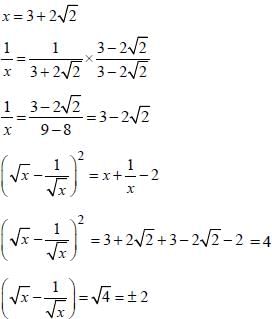
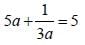
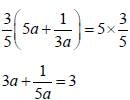
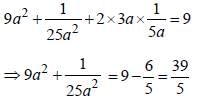
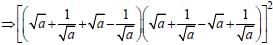
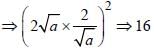
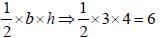
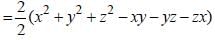
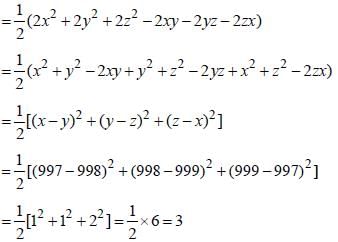
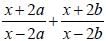
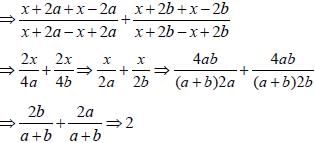
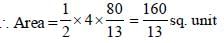
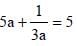
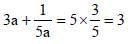
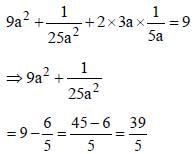
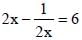
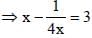 [on dividing by 2]
[on dividing by 2]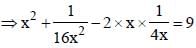 [On Squaring]
[On Squaring]