Science Practice Test - 5 - Class 5 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Science Class 5 - Science Practice Test - 5
A coconut is dispersed far away from its parent plant by
What is the adaptation by which a grasshopper protects itself from being eaten by its predator?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
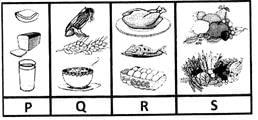
Which food items shown in the given picture are called protective foods?
The state of matter which has no fixed shape but has definite volume is the
The seeds of ___ fruit are dry and dispersed by explosion when we touch them.
Which of the following are called building blocks of rocks?
Which of the following parts of the human body has involuntary muscles?
Mrs. Kiran was on fast for the past two days, yet she is perfectly fine. Which of the following helped her to provide energy during these two days?
Which of these processes involves change of state from the liquid to gaseous state?
A simple machine used to move the object to a higher place is the
Your mother has to work in the kitchen. What adivse will you give her?
Which of the following can be called an immovable joint?
The rocks formed when existing rocks change due to heat or pressure are
|
43 videos|198 docs|45 tests
|

















