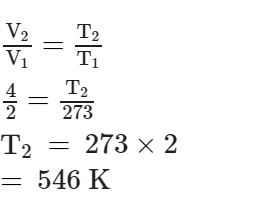Stoichiometry MCQ - 2 (Advance) - JEE MCQ
18 Questions MCQ Test - Stoichiometry MCQ - 2 (Advance)
At what temperature, given mass of a gas that occupies a volume of 2 litres at N.T.P. will occupy a volume of 4 litres, if the pressure of the gas is kept constant ?
A mixture of C3H8 (g) O2 having total volume 100 ml in an Eudiometry tube is sparked & it is observed that a contraction of 45 ml is observed what can be the composition of reacting mixture.
A mixture of 100 ml of CO, CO2 and O2 was sparked. When the resulting gaseous mixture was passed through KOH solution, contraction in volume was found to be 80 ml, the composition of initial mixture may be (in the same order)
An aqueous solution consisting of 5 M BaCl2, 58.8% w/v NaCl solution & 2m Na2 X has a density of 1.949 gm/ml. Mark the option(s) which represent correct molarity (M) of the specified ion.
[Assume 100% dissociation of each salt and molecular mass of X2– is 96]
A sample of H2O2 solution labelled as 56 volume has density of 530 gm/L. Mark the correct option(s)
representing concentration of same solution in other units. (Solution contains only H2O and H2O2)
‘2V’ ml of 1 M Na2SO4 is mixed with ‘V’ ml of 2M Ba(NO3)2 solution.
One type of artifical diamond (commonly called YAG for yttrium aluminium garnet) can be represented by the formula Y3Al5O12 [Y = 89, Al = 27]
Column I Column II
Element Weight percentage
(A) Y (P) 22.73 %
(B) Al (Q) 32.32 %
(C) O (R) 44.95 %
The recommended daily dose is 17.6 milligrams of vitamin C (ascorbic acid) having formula C6H8O6.
Match the following. Given : NA = 6 × 1023
Column I Column II
(A) O-atoms present (P) 10_4 mole
(B) Moles of vitamin C in 1gm of vitamin C (Q) 5.68 × 10_3
(C) Moles of vitamin C in 1gm should be consumed daily (R) 3.6 × 1020
At 100° C and 1 atmp, if the density of liquid water is 1.0 g cm–3 and that of water vapour is 0.0006 g
cm–3, then the volume occupied by water molecules 1 L of steam at that temperature is:
Calculate the molarity of pure water using its density to be 1000 kg m_3. [JEE' 2003]
One gm of charcoal absorbs 100 ml 0.5 M CH3COOH to form a monolayer, and there by the molarity of CH3COOH reduces to 0.49. Calculate the surface area of the charcoal adsorbed by each molecule of acetic acid. Surface area of charcoal = 3.01 × 102 m2/gm.
Calculate the amount of Calcium oxide required when it reacts with 852 gm of P4O10.[JEE 2005]
20% surface sites have adsorbed N2. On heating N2 gas evolved from sites and were collected at 0.001 atm and 298 K in a container or volume is 2.46 cm3. Density of surface sites is 6.023 × 1014/cm2 and surface area is 1000 cm2, find out the no. of surface sites occupied per molecule of N2.
Dissolving 120 g of urea (mol. wt. 60) in 1000 g of water gave a solution of density 1.15 g/mL. The molarity of the solution is: [JEE 2011]
Reaction of Br2 with Na2CO3 in aqueous solution gives sodium bromide and sodium bromate with evolution of CO2 gas. The number of sodium bromide molecules involved in the balanced chemical equation is: [JEE 2011]
A decapeptide (Mol. wt. 796) on complete hydrolysis gives glycine (Mol. Wt. 75), alanine and phenylalanine. Glycine contributes 47.0% to the total weight tto the hydrolysed products. The number of glycine units present in the decapeptideis : [JEE 2011]