TS SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 8 (History) - TS TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test TS SET Mock Test Series 2024 - TS SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 8 (History)
A battle axe type Gold Coin which pertains to the age of Samudra Gupta has been found at which of the following places in Haryana?
The ‘Saptanga Theory of State’ (Theory of Seven Limbs of the State) was propounded by :
Which of the following statements about the agrarian structure of the Gupta period are true?
(i) In the first half of the Gupta period, the king or the state claimed theoretical ownership of the land, though in practice the peasants had ownership rights.
(ii) The Poona Copper Plate of Prabhavatigupta provides us sufficient evidence for land survey during the Gupta period.
(iii) An officer called Pustapala was in charge of land revenue collection at the district level.
(iv) The Gupta inscriptions from Bengal and Bihar authorise the grantees to make a further gift of their lands to others.
(v) The Gupta land grants in central India and western India give not only fiscal rights but also rights of judicial administration to the recipients.
Select the answer from the codes given below:
Consider the following statements:
Assertion(A):- We do not find many bronze objects in prehistoric times.
Reason(R):- Tin was scarce even in ancient times.
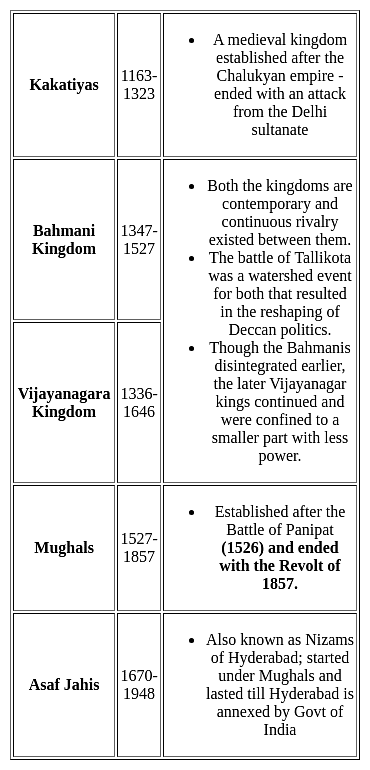
Arrange the following Kingdoms in chronological order.
a. Bahmani kingdom
b. Vijayanagara Kingdom
c. Asaf Jahis
d. Kakatiyas
e. Mughals
What was the immediate reason for the Second Carnatic War?
Assertion (A) The most remarkable development in the religious field in India from the AD 6th century was spread of tantrism.
Reason (R) Tantrism arose as a result of the large scale admission of the aboriginal people in Brahmanical society.
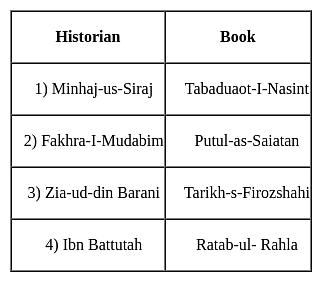
With reference to the medieval Indian history, match List I with List II, and select the correct answer by using the codes given below the lists:
List - I
I. Alberuni
II. Minhaj Siraj
III. Barani
IV. Amir Khusrau
List - II
a. Tabaqat-i-Nasiri
b. Tarikh-i-Firozshahi
c. Tahkik-i-Hind
d. Miftah-ul-Futuh
Codes:
Which among the following is not correctly matched ?
Consider the following statements with regard to Kakatiyas and select correct statements:
(A) Agriculture was the main profession during Lakatiya rule
(B) Forests cleared and new areas were brought under cultivation
(C) Land Revenue was collected both in cash and kind.
(D) Irrigation was not given importance.
Direction: Answer the following questions by selecting the correct / most appropriate options.
Statement A): Both Jaina and Buddhist monks went from place to place throughout the year, teaching people.
Statement B): Supporters of Jaina and Buddhists built temporary shelters for them in gardens, or they lived in natural caves in hilly areas.
Which among the following is NOT a correct statement in context with the Gupta Era?
Which one of the following dances is also known as the ‘Fire Dance’?
Consider the following statements about colonialism in India.
Statement (I): Each social class and group felt the effects of colonialism equally.
Statement (II): The notion of freedom was not always the same for each class and group.
Which of the following statements given below is/are correct?
With reference to Pallava dynasty, consider the following pairs:
- Seven Ratha Temple: Built by Rajasimha in eight century
- Kailashnath Temple: Built by Narasimhavarman in seventh century
Which of the pairs given above is/are incorrect?
What was the primary objective of the East India Company in India?
Consider the following events in the history of India:
1. Rise of Pratiharas under King Bhoja.
2. Establishment of Pallava power under Mahendravarman - I
3. Pala dynasty founded by Gopala.
4. Establishment of Chola power by Parantaka - I
What is the correct chronological order of the above events, starting from the earliest time? (2020)Consider the following statements regarding the relations between India and Pakistan
1) During Shimla Agreement, Indira Gandhi and Zulfikar Bhutto agreed to maintain the sanctity of LOC.
2) Lahore summit took place in the year 1997.
3) Islamabad summit was held between Rajiv Gandhi and Nawaz Sharif.
Which of these statement(s) is/are correct?
Consider the following Pairs:
 How many pair/s given above is are correctly matched?
How many pair/s given above is are correctly matched?
Which of the following statements is correct?
I. Tipu Sultan is also known as the Tiger of Mysore.
II. Tipu Sultan ruled over Mysore from 1782 to 1799.
Consider the following statements about Ashokan Edicts:
- All Ashokan edicts are written in Prakrit language
- Devanagari script was the most common script used for all writings
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Below given are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other as Reason (R):
Assertion (A): Mughal painters who migrated to the Deccan during the period of Aurangzeb were responsible for the development of various other centres of paintings in Deccan, such as Hyderabad.
Reason (R): The Deccani school of painting developed under the influence of the Mughal style from the beginning.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
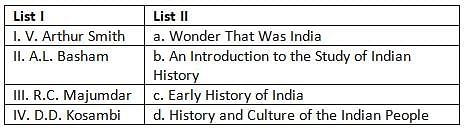
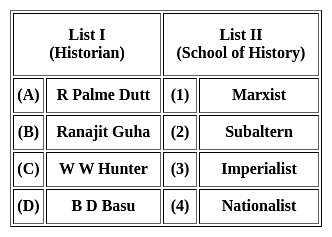
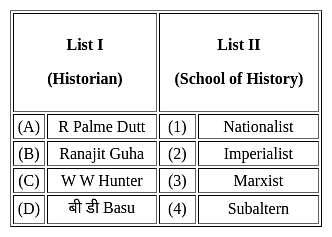
Match the historians mentioned in the List I with List II. Select the correct code given below:
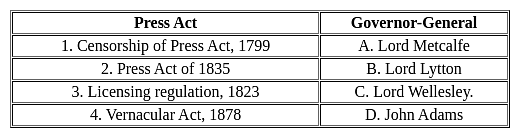
Match List I with List II, and select the correct answer by using the codes given below the lists:
Folk music
I. Lavani
II. Bhavageet
III. Padavani
IV. Naatupura Paatu
Place
a) Karnataka
b) Chhattisgarh
c) Maharashtra
d) Tamil Nadu
Codes:
|
60 tests
|