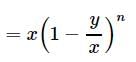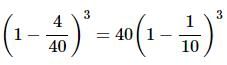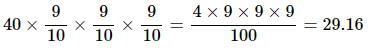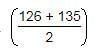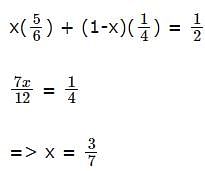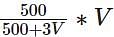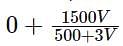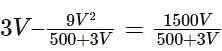Test: Alligation & Mixture- 1 - CAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - Test: Alligation & Mixture- 1
A container contains 40 litres of milk. From this container 4 litres of milk was taken out and replaced by water. This process was repeated further two times. How much milk is now contained by the container?
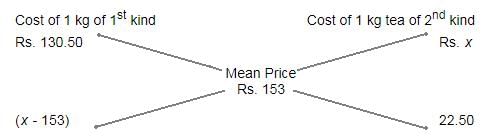
Tea worth Rs. 126 per kg and Rs. 135 per kg are mixed with a third variety of tea in the ratio 1 : 1 : 2. If the mixture is worth Rs. 153 per kg, what is the price of the third variety per kg ?
A milk vendor has 2 cans of milk. The first contains 25% water and the rest milk. The second contains 50% water. How much milk should he mix from each of the containers so as to get 12 litres of milk such that the ratio of water to milk is 3 : 5?
Two vessels A and B contain spirit and water in the ratio 5 : 2 and 7 : 6 respectively. Find the ratio in which these mixture be mixed to obtain a new mixture in vessel C containing spirit and water in the ration 8 : 5 ?
8 litres are drawn from a cask full of wine and is then filled with water. This operation is performed three more times. The ratio of the quantity of wine now left in cask to that of the water is 16:65. How much wine did the cask originally hold?
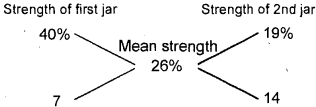
A jar is full of whiskey contains 40% alcohol. A part of this whiskey is replaced by another containing 19% alcohols and now the percentage of alcohol was found to be 26%. The quantity of whiskey replaced is:
A milkman mixes 20 litres of water with 80 litres of milk. After selling one-fourth of this mixture, he adds water to replenish the quantity that he had sold. What is the current proportion of water to milk?
Two liquids A and B are in the ratio 5 : 1 in container 1 and 1 : 3 in container 2. In what ratio should the contents of the two containers be mixed so as to obtain a mixture of A and B in the ratio 1 : 1?
There are two containers: the first contains 500 ml of alcohol, while the second contains 500 ml of water. Three cups of alcohol from the first container is taken out and is mixed well in the second container. Then three cups of this mixture is taken out and is mixed in the first container. Let A denote the proportion of water in the first container and B denote the proportion of alcohol in the second container. Then,
DIRECTIONS for the following two questions: The following table presents the sweetness of different items relative to sucrose, whose sweetness is taken to be 1.00.
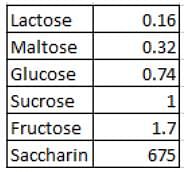
What is the maximum amount of sucrose (to the nearest gram) that can be added to one-gram of saccharin such that the final mixture obtained is atleast 100 times as sweet as glucose?
|
191 videos|131 docs|110 tests
|