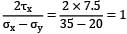Test: Analysis of Stress & Strain Level - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Strength of Materials (SOM) - Test: Analysis of Stress & Strain Level - 2
The maximum shear due to an axial compression of 100 MPa is
When a rod of cross-sectional area 100 mm2is subjected to an tensile force 6kN, the maximum shear stress in the rod will be
A body is subjected to two normal stresses 20 kN/m2 (tensile) and 10 kN/m2 (compressive) acting mutually perpendicular to each other. The maximum shear stress is
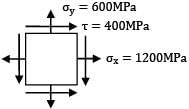
A body is subjected to a tensile stress of 1200 MPa on one plane and another tensile stress of 600 MPa on a plane at right angles to the former. If is also subjected to shear stress of 400 MPa on the same planes. The maximum shear stress will be
A Plane stressed element is subjected to the state of stress given by σx = τxy = 100 kgf/cm2 and σy = 0. Maximum shear stress in the element is equal to
The radius of Mohr’s circle for two unlike principal stresses of magnitude σ is
At a point in a stressed material, the stress system is σx = + 800N/mm2 , σy = 0 and q = 0.
The radius of the Mohr’s stress circle for this case is__________ units.
The principal stresses at a point are 150.0 MPa and − 50.0 MPa; the radius of the corresponding Mohr’s circle will be
A spherical ball of volume 106 mm3 is subjected to a hydrostatic pressure of 90 MPa. If the bulk modulus for the material is 180 GPa, the change in the volume of the ball is
An element is subjected to px = 35 MPa, py = 20 MPa and shear stress q = 7.5 MPa. Then the direction of principal stresses is
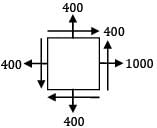
For an inclined plane in a rectangular block subjected to two mutually perpendicular normal stresses 1000 MPa and 400 MPa and shear stress 400 MPa, the maximum normal stress will be
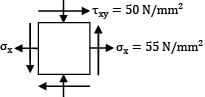
The normal stresses of 55 N/mm2 tensile and 45 N/mm2 compressive on two mutually perpendicular planes are acting at a point in a piece of elastic material. These planes also carry shear stress of 50 N/mm2. The minor principal stress will be
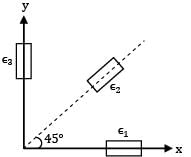
A rectangular strain rosette, shown in figure give following reading in a strain measurement task ϵP = 100 × 10−6, ϵQ = 150 × 10−6, ϵR = 200 × 10−6. The major principal strain is
If major and minor principal strains are given as 500 × 10−6 and − 200 × 10−6. Then calculate the maximum shear strain.
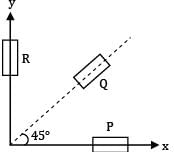
A rectangular strain rosette, shown in figure gives following reading in a strain measurement task ϵ1 = 1000 × 10−6, ϵ2 = 800 × 10−6 and ϵ3 = 600 × 10−6. The direction of the major principal strain with respect to gauge 1 is
Consider the following failure criteria and match them with their corresponding graphical representations.
P - Maximum principal stress Theory
Q - Maximum distortion energy Theory
R - Maximum principal strain Theory
I.
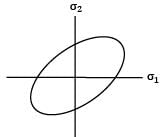
II.
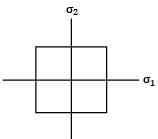
III.
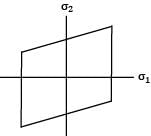
Common Data for Question No: 17 and 18 If the principal stress at a point in an elastic material are 2σ, σ and − σ/2 the properties are Syt = 200 MPa and μ = 0.3
The magnitudes of principal stresses at a point are 250 MPa tensile and 150 MPa compressive. The magnitudes of the shearing stress on a plane on which the normal stress is 200 MPa tensile and the normal stress on a plane at right angle to this plane are
The value of σ at failure according to strain energy theory
A spherical pressure shell 3.8 meters diameter and 3 mm thick is subjected to an internal pressure ‘P’. The elastic limit of the shell material in simple tension is 260 MPa. The factor of safety is to 2.8. The internal pressure, if the failure of shell is to be prevented, according to maximum shear stress theory is
The force acting on a bolt consists of two components, an axial pull of 14 kN and a transverse shear load of 7 kN. The bolt material yield strength is 340 MPa and the factor of safety is 3 then, the cross sectional area of bolt required according to maximum shear stress theory is
|
37 videos|41 docs|47 tests
|