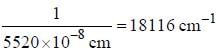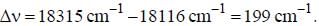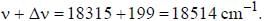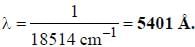Test: Atomic & Molecular Physics - 1 - Physics MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Atomic & Molecular Physics - 1
The radius of the first Bohr orbit in 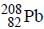 for a μ-mesic (or muonic) atom is ( The masses of μ– -meson and proton are 207 times and 1836 times respectively the mass of electron).
for a μ-mesic (or muonic) atom is ( The masses of μ– -meson and proton are 207 times and 1836 times respectively the mass of electron).
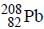 for a μ-mesic (or muonic) atom is ( The masses of μ– -meson and proton are 207 times and 1836 times respectively the mass of electron).
for a μ-mesic (or muonic) atom is ( The masses of μ– -meson and proton are 207 times and 1836 times respectively the mass of electron).The moment of inertia of the HCl molecule is 2.71 x 10-47 kg-m2. The most populated rotational level for the molecule at temperature of 600 K corresponds to
The magnetic moment of an electron moving in a circular orbit of radius r about a proton is
where = 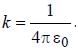
where =
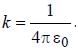
The normal Zeeman splitting in the mercury 4916 Å line in a magnetic field of 0.3 T is
The common wave number difference in the two successive rotational lines is
For high principal quantum number (n) for hydrogen atom the spacing between the neighbouring energy level is proportional to
The Lande g-factor for the 3P2 level of an atom is______________
(Round off to one decimal places)
The Bohr model gives the value for the ionization potential of Be+++ ion as__________10-1 eV
(Round off to two decimal places)
The line width of a spectral line of 600 mil wavelength emitted from a level of a lifetime of 10-8 sec, is__________×10-15 m (up to two decimal places)
The radiations given offby the Hg atoms returning to their normal states were studied by Frank and Heitz and
a line was observed at 2573 Å. The excitation potential for Hg is________volt (upto one decimal place)
The spacing of a series of lines in the microwave spectrum of AIH is constant at 12.604 cm-1. The moment of
inertia of the AIH molecule is_______x 10-47 kg/m2. (upto two decimal places)
If the Kα -radiation o f Mo (Z = 42) lias a wavelength o f 0.71 A. the wavelength o f the corresponding radiation for Cu (Z = 29) is Å. (upto two decimal places)
A positroniiun atom is system consisting of a position and an electron revolving about their common center of mass, which lies halfway between them. The ratio of the wavelength of the first line of the Balmer series of positroniumatomto the wavelength of the first line of the Balmer seiies of hydrogen atom is
A sample of ordinary hydrogen 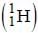 gas in a discharge tube was seen to emit the usual Balmer spectrum. On careful examination however, it was found that the Hα -line in the spectrum was split into two fine lines, one an intense line at 6562.80 Å and the other at 6561.01 Å. From this, one can conclude that the gas sample had a small impurity of
gas in a discharge tube was seen to emit the usual Balmer spectrum. On careful examination however, it was found that the Hα -line in the spectrum was split into two fine lines, one an intense line at 6562.80 Å and the other at 6561.01 Å. From this, one can conclude that the gas sample had a small impurity of
The gBe+ ion has a nucleus with spin 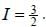 The possible values of the hypofine quantum number F for the 2S1/2 electric level are
The possible values of the hypofine quantum number F for the 2S1/2 electric level are
An atomic magnetic dipole having orbital magnetic moment of 1 Bohr magneton is aligned parallel to a external magnetic field of 1 Tesla. The energy required to turn the dipole to align it antiparallel to the field is_________x 10-4 eV. (upto two decimal places)
In the doublet splitting of the first excited state. 22P3/2 — 2 2P1/2 of He+ is 5.84 cm-1. the corresponding separation for H is
Assume that the H2 molecule behaves like a harmonic oscillator with a force constant k = 573 N/m the vibrational quantum number, corresponding to its dissociation energy 4.5 eV, is
If the exciting line in an experiment is 5460 Å and the stokes line is at 5520 Å. the wavelength (inÅ) of the antistokes line is__________Å. (should be an integer)


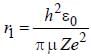 ....(i) where μ is reduced mass.
....(i) where μ is reduced mass.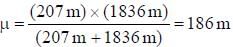 , where m is the mass o f the electron.
, where m is the mass o f the electron.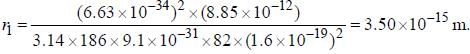
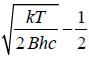 , where B is rotational constant.
, where B is rotational constant.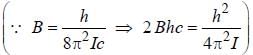
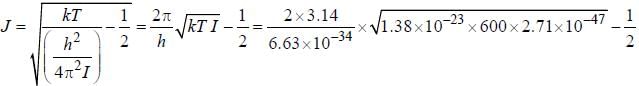

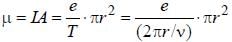 ...(i)
...(i)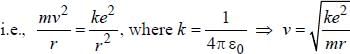 ...(ii)
...(ii)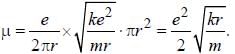
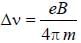 ....(i)
....(i)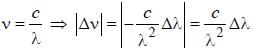
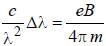
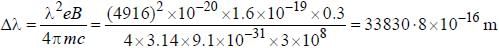
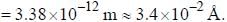
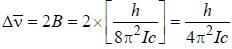
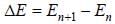
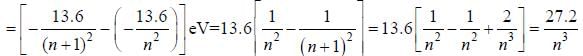
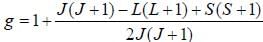 ...(i)
...(i)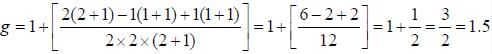
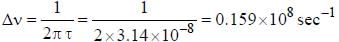
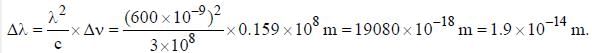
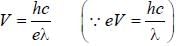
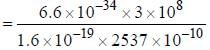

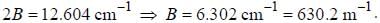
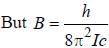 , where I is the moment of inertia of the rotating molecule.
, where I is the moment of inertia of the rotating molecule.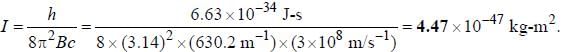
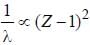
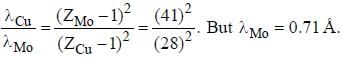
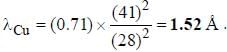
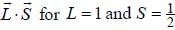 is
is 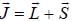
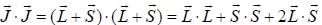
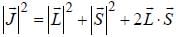
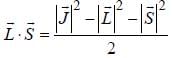
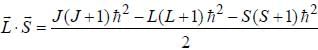
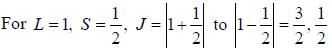
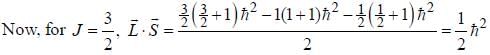
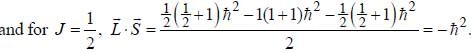
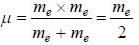
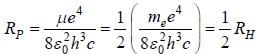 ...(1)
...(1)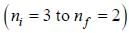 of positronium a tom is given by
of positronium a tom is given by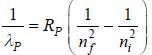
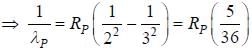
 ....(2)
....(2)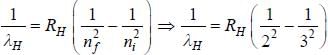
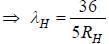
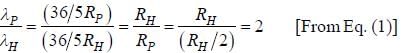
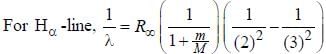
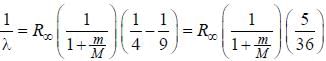
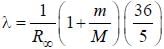 .....(i)
.....(i)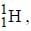 the
the 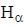 -line is at 6562.80 Å. thus equation (i) implies with M = 1836 m, λ = 6562.80 Å;
-line is at 6562.80 Å. thus equation (i) implies with M = 1836 m, λ = 6562.80 Å;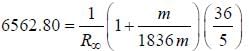 ...(ii)
...(ii)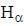 - line is at 6561.01 Å thus M = x x 1836 m (H ere, we have assum ed the m ass of nucleus of unknown impurity equal to x times mass of proton or hydrogen nucleus). λ = 6561.01 Å;
- line is at 6561.01 Å thus M = x x 1836 m (H ere, we have assum ed the m ass of nucleus of unknown impurity equal to x times mass of proton or hydrogen nucleus). λ = 6561.01 Å;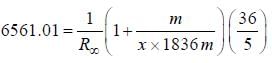 ...(iii)
...(iii)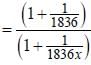
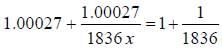
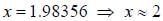
 Out o f the given options, nucleus
Out o f the given options, nucleus 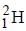 has the mass equal to two times the nuclear mass of
has the mass equal to two times the nuclear mass of 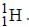
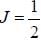
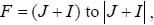 with decrease o f unity.
with decrease o f unity.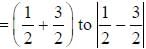
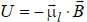
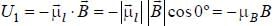 ...(i)
...(i)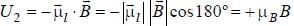 ...(ii)
...(ii)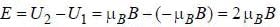

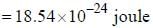
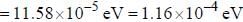
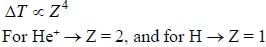
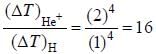
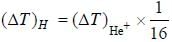
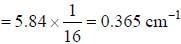
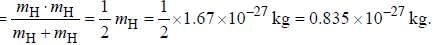
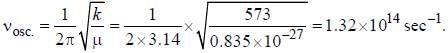
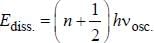
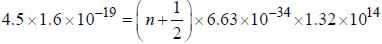
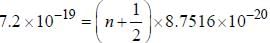
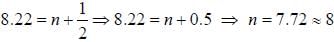
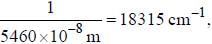 and that of the stokes line is
and that of the stokes line is