Test: Basic Features of The Constitution of India- 1 - Humanities/Arts MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Basic Features of The Constitution of India- 1
Choose the most appropriate option.
Which one of the following is not a Directive Principle of State Policy under Part IV of the Constitution of India?
Voting in the Estates General was conducted on the principle of
Fundamental rights or basic human rights are _____.
Choose the most appropriate option.
Which among the following does not belong to the 'right to freedom of religion'?
In which year the first meeting of Constituent Assembly took place?
Which one is not a Directive Principle?
Which of the following right is available under the Indian Constitution?
(This question has multiple correct options)
Match the following while selecting the right code.
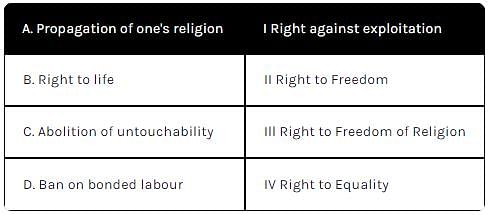
Right to work is a part of _____.
_____ acts as a custodian of our Constitution and protects our Fundamental Rights.


















