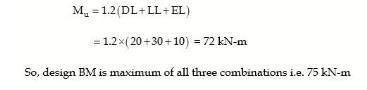Test: Beams & Slabs - 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Beams & Slabs - 1
A doubdly reinforced beam is considered less economical than a singly reinforced beam because.
The maximum percentage of moment redistribution allowed in RCC beams is (UP/AE 2017)
Partial safely factor for concrete and steel are 1.5 and 1.15 respectively, because
In the design of two-way slab restrained at all edges, torsional reinforcement required is
A reinforced concrete slab is 75 mm thick. The maximum size of reinforced bar that can be used is of
In the limit state method, balanced design of a reinforced concrete beam gives
In case of simply supported beam, the clear distance between lateral restrains shall not exceed
(UP/AE 2005)
The prestressed concrete slab systems are ideally suited for __________
In case of 2-way slab, the limiting deflection of the slab is
The main reinforcement of a RC slab consists of 10 mm bars at 10 cm spacing. If it is desired to replace 10 mm bars by 12 mm bars, then the spacing of 12 mm bars should be
In a reinforced concrete T-beam (in which the flange is in compression). The position of neutral axis will
The maximum depth of neutral axis for a beam with 'd' as the effective depth, in limit state method of design for Fe 415 steel is
A reinforced concrete beam is subjected to the following bending moments:
Dead load — 20 kN-m
Live load — 30 kN-m
Seismic load — 10 kN-m
The design bending moment for limit state of collapse is
In a cantilever beam carrying gravity load, main reinforced is provided
A doubly reinforced concrete beam has effective cover 'd' to the centre of compression reinforcement. 'xu' is the depth of neutral axis, and 'd' is the effective depth to the centre of tension reinforcement. What is the maximum strain in concrete at the level of compression reinforcement?
Consider the following statement:
In an under-reinforced concrete beam,
1. actual depth of neutral axis is less than the critical depth of neutral axis.
2. concrete reaches ultimate stress prior to steel reaching the ultimate stress.
3. moment of resistance is less than that of balanced sections.
4. lever arm of resisting couple is less than of balanced sections.
Which of those statements is/are correct?
Two rectangular under-reinforced concrete beam sections X and Y are similar in all aspects except that the longitudinal compression reinforcement in section Y is 10% more. Which one of the following is the correct statement?
In the case of a continuous RC beam,in order to obtain the maximum positive span moment,where should the live load be placed?
Usually stiffness of a simply supported beam is satisfied if the ratio of its span to depth does not exceed which one of the following?
In a singly reinforced concrete beam section, maximum compressive stress in concrete and tensile stress reach their permissible stressess simultaneously. What is such a section called?
What shall be the maximum area of reinforcment
(i) in compression and
(ii) in tension to be providedin an RC beam, respectively, as per IS:456?
In limit state design method, the moment of resistance for a balanced section using M20 grade concrete and HYSD steel of grade Fe 415 is given by Mu,lim = Kbd2, what is the value of K?
How is the deflection in RC beams controlled as per IS:456?
What is the adoptable maximum spacing between vertical stirrups in an RCC beam of rectangular cross-section having an effective depth of 300 mm?