Test: Bihar Specific (Role of Bihar in Freedom Struggle) - Software Development MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Bihar Specific (Role of Bihar in Freedom Struggle)
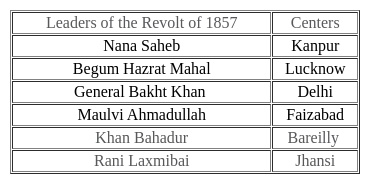
Who was the leader of the revolt of 1857 in Jagdishpur (Bihar)?
When did the Santhal rebellion start?
Who was the Commissioner (Commissioner) of Patna at the beginning of the Revolt of 1857 AD in Bihar?
Consider the following statements with respect to the Champaran Satyagraha :
1. The reason for the discontent among the farmers was the low remuneration they received for the crop.
2. Raj Kumar Shukla persuaded Mahatma Gandhi to visit Champaran and work for the oppressed peasants.
3. The predominant system of Indigo cultivation in Champaran was the tinkathia system.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Which of the following statement is/are correct about the Champaran Satyagraha?
1. It was started on 1 April 1918.
2. The Champaran Satyagraha was the first Satyagraha movement inspired by Gandhi.
Select the correct answer using the code given below
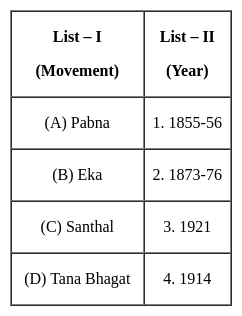
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists: