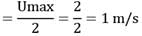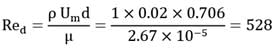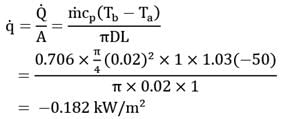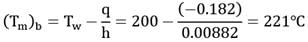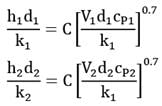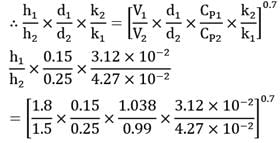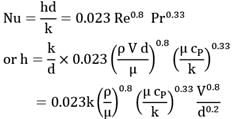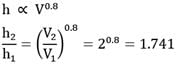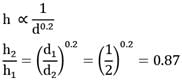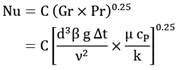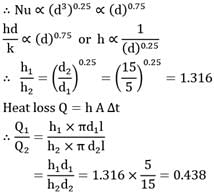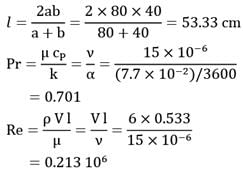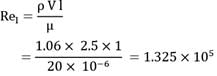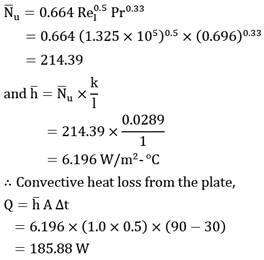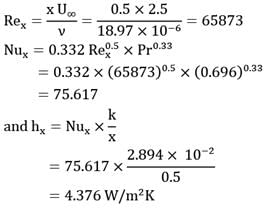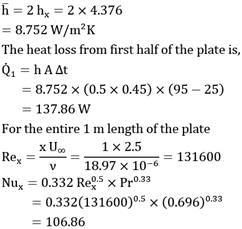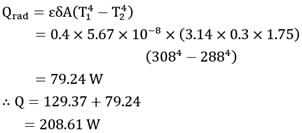Test: Convective Heat Transfer: One Dimensional Level - 3 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Convective Heat Transfer: One Dimensional Level - 3
Hot air flowing through a metal pipe of 20 mm diameter is cooled at a constant rate per unit length of pipe. At a particular section (a), the air velocity in the centre of the pipe is found to be 2 m/s and the wail temperature, as measured by a thermocouple on the inner surface of the pipe, is 250°C . At the section (b), situated 1 m downstream from the section (a), the wall temperature is found to be 200°C. The mean air temperature at section (b) is _________.
cp = 1.03 kj/kg. K, k = 4.04 x 10-5 kW/m2K,
At 500 K, p = 0.706 kg/m3 & p = 2.67 X 10-5 kg/m-sec
cp = 1.03 kj/kg. K, k = 4.04 x 10-5 kW/m2K,
At 500 K, p = 0.706 kg/m3 & p = 2.67 X 10-5 kg/m-sec
Air flows at 1.8 m/s past a 15 cm diameter pipe in a direction normal to the axis. The pipe surface is at 30°C and it receives 4.95 kW/m2 of heat from the air at 250°C temperature. The convective heat transfer coefficient is prescribed by the relation.
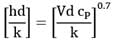
Under similar operating conditions, make calculations for the heat loss from carbon dioxide at 200°C when it flows at 1.5 m/s normal to a 25 cm diameter pipe at 25°C.
The relevant thermo-physical properties for air and carbon dioxide are For air at 250°C
cP = 1.038 kJ/kgK
k = 4.270 x 10-2 W/mK
For CO2 at 200°C
cP = 0.99 kJ/kgK
k = 3.12 x 10-2 W/mK
Predict your answer in kW/m2 correct upto two decimal places.
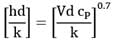
Under similar operating conditions, make calculations for the heat loss from carbon dioxide at 200°C when it flows at 1.5 m/s normal to a 25 cm diameter pipe at 25°C.
The relevant thermo-physical properties for air and carbon dioxide are For air at 250°C
cP = 1.038 kJ/kgK
k = 4.270 x 10-2 W/mK
For CO2 at 200°C
cP = 0.99 kJ/kgK
k = 3.12 x 10-2 W/mK
Predict your answer in kW/m2 correct upto two decimal places.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The effect of following conditions on the average value of heat transfer coefficient in flow through a tube:
(i) two-fold increase in flow velocity by varying mass flow rate;
(ii) two-fold increase in the diameter of tube, the flow velocity is maintained constant by a change in the rate of liquid flow It may be presumed that there is no change in the temperatures of the liquid and the tube wall, and that the flow through the tube is turbulent in character.
Given Nu = 0.023 Re0.8 Pr0.4
(i) two-fold increase in flow velocity by varying mass flow rate;
(ii) two-fold increase in the diameter of tube, the flow velocity is maintained constant by a change in the rate of liquid flow It may be presumed that there is no change in the temperatures of the liquid and the tube wall, and that the flow through the tube is turbulent in character.
Given Nu = 0.023 Re0.8 Pr0.4
Two horizontal steam tubes with diameters 5 cm and 15 cm are so laid in a boiler house that any mutual heat effect is precluded. The tubes are at the same surface temperature of 500°C while the ambient air is at 50° C. Work out the ratios of the heat loss rates from one meter length of the tubes. Given Nu = C(Gr x Pr)0.25 where C is a constant. Predict your answer correct upto two decimal places.
Air at atmospheric pressure and 20°C flows with 6 m/s velocity through main trunk duct of air conditioning system. The duct is rectangular in cross-section and measures 40 cm x 80 cm. Determine heat loss rate (in W) per meter length of duct corresponding to unit temperature difference. The relevant thermo-physical properties of air are
v = 15 x 10-6 m2/s
α = 7.7 x 10-2 m2/hr
and k = 0.026 W/m-°C
Given Nu = 0.023 Re0.8 Pr0.4
Air at 2 bar pressure and 200°C temperature gets heated as it flows through 2.5 cm diameter tube with a velocity of 10 m/s. A constant heat flux condition is maintained at the wall and wall temperature is 20°C above the air temperature all along the length of the tube. Make calculations for the heat transfer (in w) per unit length of the tube. Also determine the increase in bulk temperature over a 3 meter length of the tube. If the flow is turbulent then the appropriate correlation for the convection coefficient is
Nu = 0.023 (Re)0.8 (Pr)0.4
The thermo-physical properties of air are as follows.
μ = 2.57 x 10-5 Ns/m2
k = 0.0385 W/m- °C
and cP = 1025 J/kgK
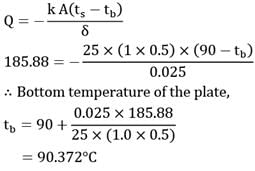
Atmospheric air at 30°C temperature and free stream velocity of 2.5 m/s flows along the length of a flat plate which is maintained at a uniform temperature of 90°C. The length, width and thickness of the plate is 100 cm, 50 cm and 2.5 cm. If thermal conductivity of the plate material is 25W/m-°C, make calculations for
(a) heat lost by the plate (in W)
(b) temperature of bottom surface of the plate for steady state conditions (in °C)
Properties - Take thermo physical properties of air as;
p = 1.06 kg/m3
CP = 1005 J/kgK
Pr = 0.696
k = 0.0289 W/m°C
and, μ = 20 x 10-6 Kg/m-s
A thin flat plate of length 1 = 1 m and breadth b = 0.45 m is exposed to a flow of air parallel to its surface. The velocity and temperature of the free stream flow of air are respectively U∞ = 2.5 m/s and t∞ = 25°C. If temperature at the surface of plate is ts = 95°C, estimate the heat loss from 50 cm length of plate measured from the trailing edge.
At the mean film temperature
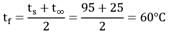
The thermo-physical properties of air are
ρ = 1.060 kg / m3
k = 2.894 x 10-2W/mK
v = 18 .97 x 10-6m2/s
and Pr = 0.696
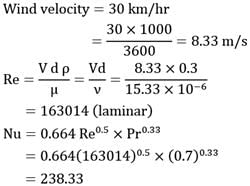
Calculate the rate of heat loss from a human body which may be considered as a vertical cylinder 30 cm in diameter, and 175 cm high while standing in a 30 km/hr wind at 15°C. The surface temperature of the human is 35°C At the mean film temperature,
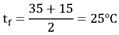
The thermo-physical properties of air are
v = 15.33 x 10-6 m2/s
k = 0.0263 W/m - ° C
Pr = 0.7
Given, Nu = 0.13 (Gr x Pr)0.33
Given: Lubricating oil (ρ = 865 kg/m3, k = 0.1 4 W/m K, cp = 1.7 8 kj /kg K,) and v = 9 x 10-6 m2/ s at 60°C enters a 1 cm dia tube with a velocity of 3.5 m /s. Tw = 30 °C, constant. To find: The tube length required to cool the oil to 45°C given Nud = 0.023 (Red)0.8( Pr)0.3 if flow is turbulent.