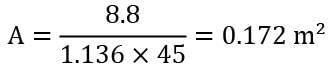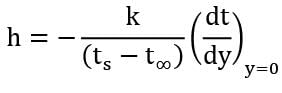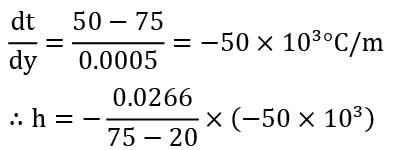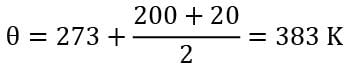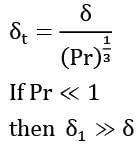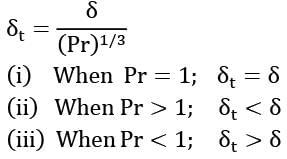Test: Convective Heat Transfer: One Dimensional Level - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Convective Heat Transfer: One Dimensional Level - 1
Match List-I (Flow pattern) with List-II (Situation) and select the answer using the codes given below the lists.
List-I
(A) 
(B)
(C)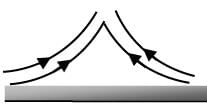
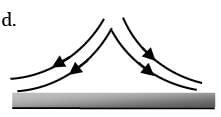
List-II
1. Hot horizontal plat
2. Cool horizontal plate
3. Hot vertical plate
4. Cool vertical plate





Forced air flows over the surface of heat exchanger in a room heater, resulting in a convective heat transfer coefficient 1.136kW/m2k. The surface temperature of heat exchanger may be considered constant at , and the air is at an ambient temperature 20oC. Determine the heat exchanger surface area required for 8.8 kW of heating (in m2) correct upto 3 decimal places.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
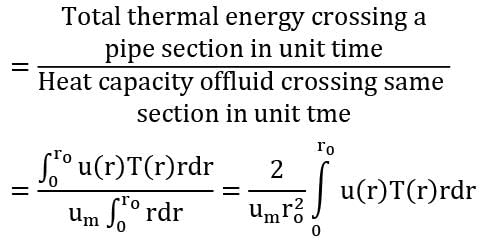
Consider a hydro-dynamically fully developed flow of cold air through a heated pipe of radius ro . The velocity and temperature distributions in the radial direction are given by u(r) and T(r) respectively. If um , is the mean velocity at any section of the pipe, then the bulk-mean temperature at that section is given by
Air at 20०C flows over a flat plate maintained at 75०C . Measurements show that temperature at a distance of 0.5 mm from the surface of the plate is 50०C. Presuming thermal conductivity of air as 0.0266 W / m-deg, estimate the value of local heat transfer coefficient, (in W/m2K ) correct upto two decimal places.
Match List-I (Type of heat transfer) with List-II (Governing dimensionless parameters) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists.
List-I
a. Forced convection
b. Natural convection
c. Combined free and forced convection
d. Unsteady conduction with convection at surface
List-II
1. Reynolds, Grashoff and Prandtl number
2. Reynolds and Prandtl number
3. Fourier number and Biot number
4. Prandtl number and Grashoff number
A horizontal heated plate at 200०C and facing upwards has been placed in still air at 20०C . If the plate measures 1.25m x 1m , make calculations for the heat loss by natural convection. The convective film coefficient for free convection is given by the following empirical relation h=0.32 (θ)0.25W/m2K
Where θ is the mean film temperature in Kelvin. Predict your answer in watts correct upto two decimal places.
In a convective heat transfer situation Reynolds number (Re) is very large but the Prandtl number (Pr) is so small that the product of Re and Pr is less than one. In such a condition which one of the following is correct?
Nusselt number for a pipe flow heat transfer coefficient is given by the equation NuD = 4.36. Which one of the following combinations of conditions do exactly apply for use of this value?
For a fluid having Prandtl number equal to unity, how are the hydrodynamic boundary layer thickness δ and the thermal boundary layer thickness δ t related?
Hot air at 150oC flows over a flat plate maintained at 50oC. If the corresponding convection heat transfer coefficient is 75 W/m2K, the heat gain rate by the plate through an area 2m2 of will be