Test: Distinction of Alcohols (February 8) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for NEET Preparation - Test: Distinction of Alcohols (February 8)
Which of the following alcohols produce turbidity immediately when reacted with conc. HCl and ZnCl2?
An organic compound X (C7H16O) on treatm ent with concentrated HCI solution forms immediate turbidity even in the absence of ZnCl2. Also, X is resolvable into enantiomers. The correct statement concerning X is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following is least likely to form turbidity with HCI in the presence of ZnCI2 at room temperature?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 9-12) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Which reagent(s) can be used to differentiate between 2-pentanol and 1-pentanol?
Alcohols given below that behaves like 1°-aliphatic alcohol in Lucas test is/are
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-15) This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
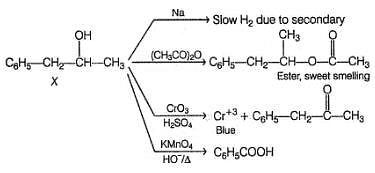
An organic compound X (C9H12O) gives the following reactions :
i. Na - Slow gas bubble formation
ii. Acetic anhydride - Pleasent smelling liquid
iii. CrO3-H2SO4 - Blue-green solution
iv. Hot KMnO4 - Benzoic acid
v. Br2-CCI4 - No decolouration
vi. I2 + NaOH - Yellow solid is formed
vii. X rotates the plane polarised light
Q.
The structure of X is
An organic compound X (C9H12O) gives the following reactions :
i. Na - Slow gas bubble formation
ii. Acetic anhydride - Pleasent smelling liquid
iii. CrO3-H2SO4 - Blue-green solution
iv. Hot KMnO4 - Benzoic acid
v. Br2-CCI4 - No decolouration
vi. I2 + NaOH - Yellow solid is formed
vii. X rotates the plane polarised light
Q.
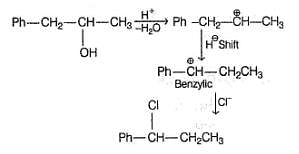
If X is treated with HCI in the presence of ZnCI2, the major product would be
An alcohol X (C7H16O) gives immediate turbidity with HCI/ZnCI2 and can be resolved into enantiomers. Also X has a tertiary hydrogen. How many CH3— groups are present in X?
An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both enantiomers and diastereomers. X gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution. With CrO3 - H2SO4 , X is converted into C7H14O (Y) which has enantiom ers but not diastereom ers. X on refluxing with H2SO4 isomerises to Z which neither gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine nor changes colour of CrO3 - H2SO4 . What is the minim um number of carbons that can be present in the parent chain of X ?
An organic compound C4H10O (X) on reaction with I2/red-P give s C4H9I which on further reaction with AgNO2 gives C4H9NO2 (Y). Y on treatment with HNO2 forms a blue solution which turns to red on making solution slightly alkaline. The possible identity of X is
|
12 docs|366 tests
|