Test: ER-Model- 2 - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Question Bank for GATE Computer Science Engineering - Test: ER-Model- 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
It is desired to design an object-oriented employee record system for a company. Each employee has a name, unique id and salary. Employees belong to different categories and their salary is determined by their category. The functions get Name, get ld and compute Salary are required. Given the class hierarchy below, possible locations for these functions are:
1. getld is implemented in the superclass.
2. getId is implemented in the subclass.
3. getName is an abstract function in the superclass.
4. getName is implemented in the superclass.
5. getName is implemented in the subclass:
6. getSalary is an abstract function in the superclass.
7. getSalary is implemented in the superclass.
8. getSalary is implemented in the subclass
Choose the best design
1. getld is implemented in the superclass.
2. getId is implemented in the subclass.
3. getName is an abstract function in the superclass.
4. getName is implemented in the superclass.
5. getName is implemented in the subclass:
6. getSalary is an abstract function in the superclass.
7. getSalary is implemented in the superclass.
8. getSalary is implemented in the subclass

Choose the best design
Let E1 and E2 be two in an E/R diagram with simple single-valued attributes R1, and R2 are two relationship between E1, and E2, where R1, is one-to many and R2 is many-to-many. R1, and R2 do not have any attributes of their own. What is the minimum number of tables required to represent this situation in the relational model?
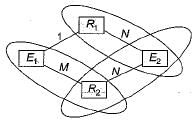
Consider the following ER diagram:
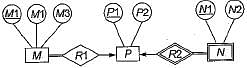
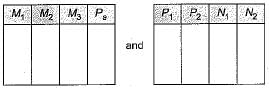
The minimum number of table needed to represent M, N, P, R1, R2 is.
Consider the following ER diagram:
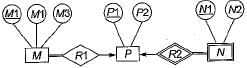
Which of the following is a correct attribute set for one of the tables for the correct answer to the above question?
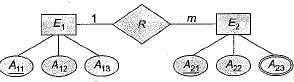
Consider the following entity relationship diagram (ERD), where two entities E1 and E2 have a relation R of cardinality 1 : m.
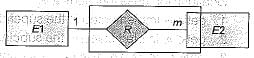
The attributes of E1 are A11, A12 and A13where , A11 is key attribute. The attributes of E2 are A21, A22, and A23 where A21 is the key attribute and A23 is a multi-valued attribute. Relation R does not have any attribute. A relational database containing minimum number of tables with each table satisfying the requirements of the third normal form (3NF) is designed from the above ERD. The number of tables in the database is
Consider the relation Student (name, sex, marks), where the primary key is shown underlined, pertaining to students in a class that has at least ( One boy and one girl. What does the following relational algebra expression produce? [Note: p is the rename, operator]

An ________ is a set of entities of the same type that share the same properties, or attributes.
The descriptive property possessed by each entity set is _________
|
63 videos|8 docs|165 tests
|
|
63 videos|8 docs|165 tests
|


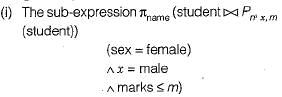
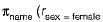 (student)) gives the name of all the female student from (i) and
(student)) gives the name of all the female student from (i) and














