Test: Education & Leadership (Growth and Development - I) - Software Development MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Education & Leadership (Growth and Development - I)
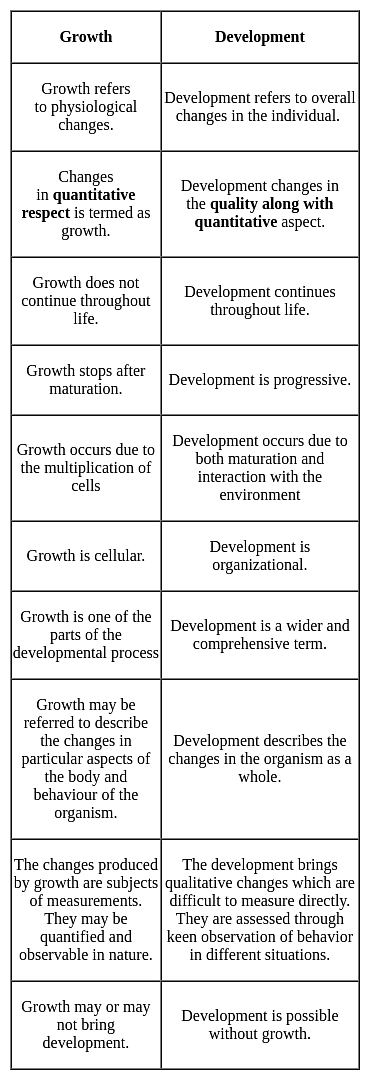
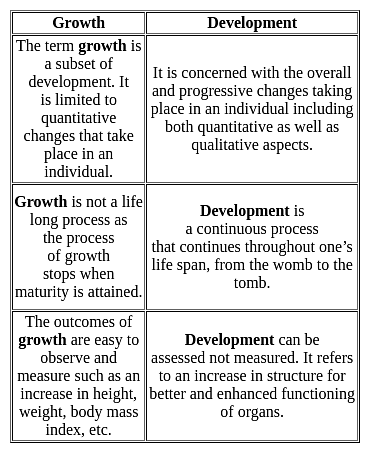
Which of the following is true for the processes of growth and development?
The process of an individual’s capacities quantitatively should be termed as
Development is a continuous process, but growth does not continue throughout life, it stops when ______ has been attained.
Which of the following statements is most appropriate in relation to adolescence?
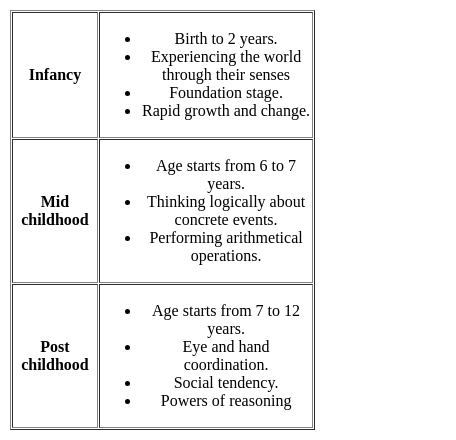
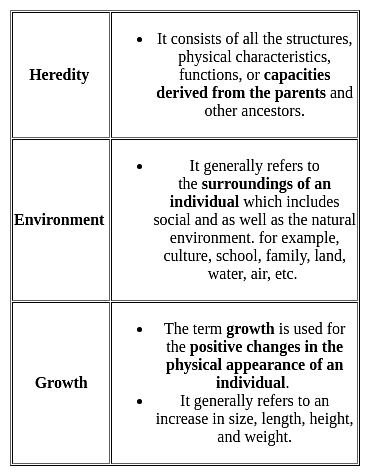
Most children can sit without support by 7 months of age, stand with support by 8 months and walk by one year. Once the underlying physical structure is sufficiently developed, proficiency in these behaviors requires an adequate environment and little practice. However, special efforts to accelerate these behaviors do not help if the infant is maturational and not ready. The bold word can be attributed to the importance of:
The result of the interaction between maturation and learning is
Which of the principles of development is defined by the below given example?
Sufi has appropriate weight and height for her age. She also has a well-developed language ability that enables her to communicate with everyone. She is loved by all and has positive
self-esteem.
In the evening, Kalpesh went to a nearby park to observe young/small children playing (2- 6 years of age) usually escorted by their parents. He noticed the interacting patterns of parents and their children in the park. Two situations were observed by Kalpesh.
Situation 1: A couple scolded the child when she was asking for the ice cream.
Situation 2: A couple was playing hide and seek with their child.
These two situations are examples of which type of socialization