Test: Electoral Politics - UGC NET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electoral Politics
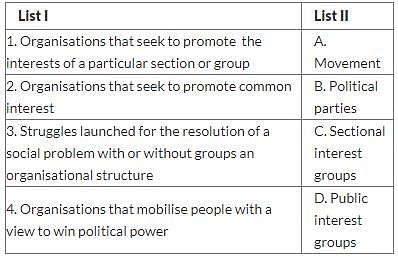
Match List I (organisations and struggles) with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:

Which of the following are the issues of debate in electoral politics?
A. Electronic voting machine
B. One nation, one election
C. Single-member election commission
D. Introduction of the two-children norm for eligibility to contest local elections
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The demand for 'Harit Pradesh' is related to which one of the following regions in India?
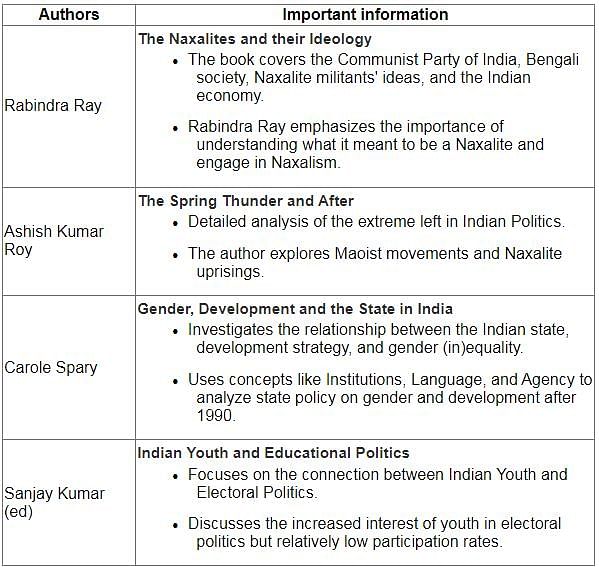
The book “Game of Votes: Visual Media Politics and Elections in the Digital Era” is writtern by ____
Match List I with List II
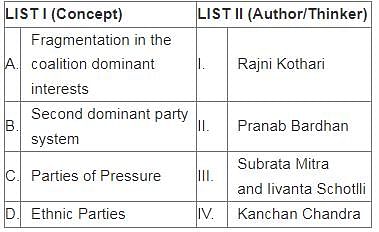
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Match List I with List II
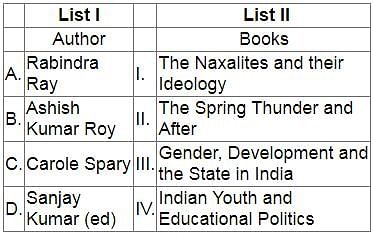
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Read the following statements about the 'Dravidian movement':
(A) This was an all-India movement in Indian politics.
(B) The Dravidian movement led to the formation of o Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (DMK).
(C) It used democratic means like public debates and the electoral platform to achieve its ends.
Choose the correct option.
Which of the following have caused the growth of Co-operative federalism in India?
(A) Union-State collaboration in economic matters
(B) Union-State legislative relations
(C) Compulsion of developmental finance
(D) Dynamics of electoral politics
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Which of the following does NOT characterise electoral politics in India today?
What is the correct chronological sequence of the below ? Choose the right answers from the codes:
A. Joint Parliamentary Committee on Reform of Electoral law
B. Goswami Committee on electoral Reforms
C. Tarkunde Committee on Electoral Reforms
D. Election Commission's campaign against criminalization of politics.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: