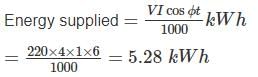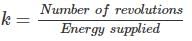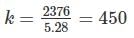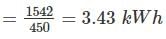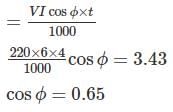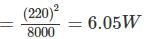Test: Electrical & Electronic Measurements- 4 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electrical & Electronic Measurements- 4
A 200 V, 5 A d.c. energy meter is tested at its marked ratings. The resistance of the pressure circuit is 8000 Ω and that of current coil is 0.1 Ω. The power consumed when testing the meter with phantom loading with current circuit excited by a 6 V battery is?
The meter constant of a single phase 240V induction watt-hour meter is 500 revolutions per kWh. The sped of the meter disc for a current of 15A at 0.6 P.f lagging will be ------ (in rpm)
The braking torque provided by a permanent magnet in a single phase energy meter is proportional to the
i) square of the flux of the permanent magnet
ii) speed of the meter
iii) distance of he permanent magnet from the center of the revolving disc
Q. Which of the above statements are correct.
i) square of the flux of the permanent magnet
ii) speed of the meter
iii) distance of he permanent magnet from the center of the revolving disc
Q. Which of the above statements are correct.
Which one of the following defects is responsible for creeping in an induction type energy meter?
A 230 V, single phase watt hour meter has a constant load of 6 A passing through it for 8 hours at unity power factor. If the meter disc makes 2400 revolutions during this period. What is the power factor of the load if the number of revolutions made by the meter are 1800 when operating at 230 V and 8 A for 6 hours?
In a vibrating reed frequency meter the natural frequencies of two adjacent reeds have a difference of
The constant for a three phase, 3 element integrating wattmeter is 0.12 revolution of disc per kWh. If the meter is normally used with a potential transformer of ratio 22,000/110V and a current transformer of ratio 500/5A; find the error expressed as a percentage of the correct reading from the following test figures for the instrument only
Line voltage = 100 V; current = 5.25 A; power factor = 1
Time to complete 40 revolutions = 61s.
A single phase energy meter operating on 220 V and 8 A for half day i.e. 12 hours makes 3200 revolutions. If the meter constant = 600 revolutions/kwh, then the power factor of the load will be
A 220 V, single phase, watt hour meter has a constant load of 4 A passing through it for 6 hour at unity power factor. The meter disc makes 2376 revaluation during this period. If the number of revolution made by the meter are 1542 when operating at 220 V and 6 A for 4 hours, then power factor of the load would be
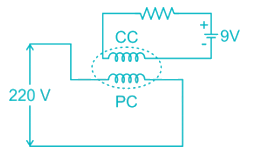
A 220V, 10 A dc energy meter is tested for its name plate ratings. Resistance of the pressure coil circuit is 8000 Ω and that of current coil itself is 0.12 Ω calculate the energy consumed when testing for a period of 1 hour with phantom loading with the current coil circuit excited by a separated 9 V battery.




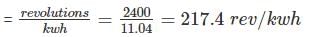
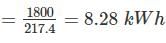
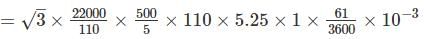 = 338.97 kWh
= 338.97 kWh 
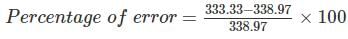 = −1.66% = 1.66% low
= −1.66% = 1.66% low