Software Development Exam > Software Development Tests > Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Software Development MCQ
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Software Development MCQ
Test Description
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues)
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Software Development exam syllabus.The Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) MCQs are made for Software Development 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) below.
Solutions of Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) questions in English are available as part of our course for Software Development & Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) solutions in
Hindi for Software Development course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Software Development Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) | 20 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for Software Development preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Software Development Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 1
Which process is responsible for Global warming?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 1
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 2
Global environmental problem is mainly due to:
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 2
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 3
The global warming has resulted:
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 3
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 4
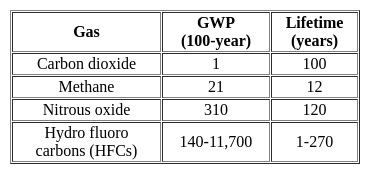
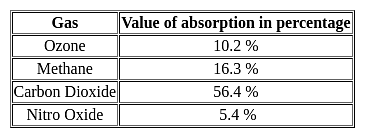
Which gas has highest global warming potential?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 4
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 5
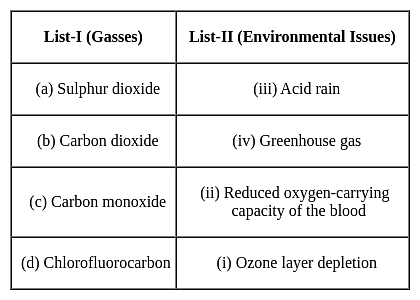
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below:

Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 5
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 6
What type of radiation is trapped on the earth’s surface by the green house effect ?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 6
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 7
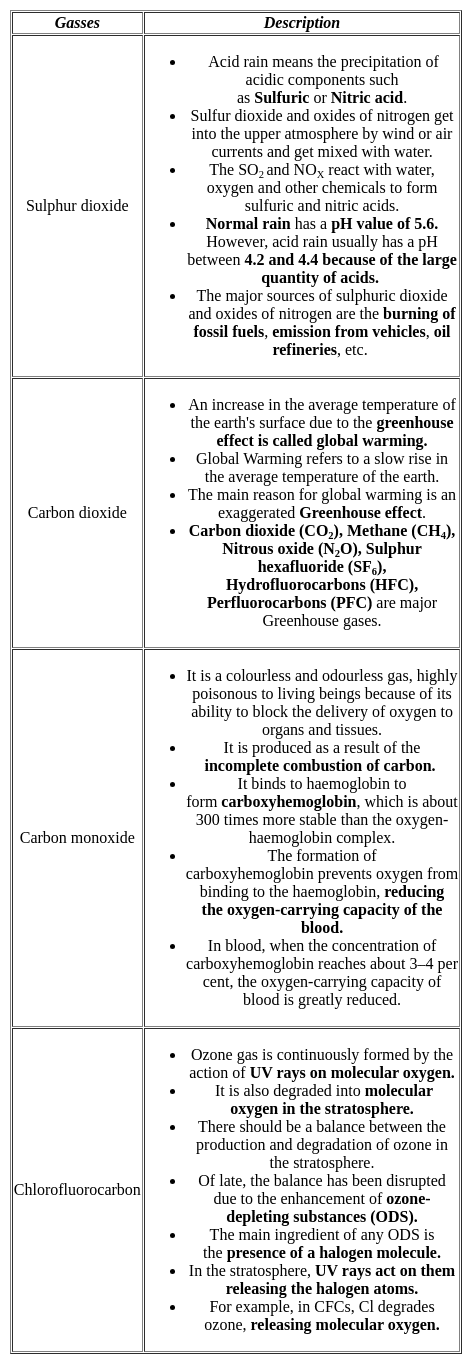
Taj Mahal is getting damaged due to the effects of
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 7
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 8
Which of the following is/are effects of ozone depletion?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 8
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 9
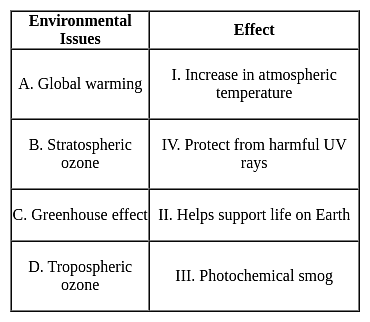
Match the following environmental issues with their related effect.
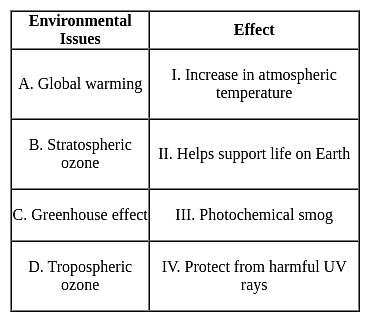
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 9
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 10
Identify environmental issues which are local in nature:
(i) Depletion of ozone layer
(ii) Lake pollution
(iii) Soil erosion
(iv) Climate change
(v) Water logging
(vi) Solid Waste Management
Select the answer from the options given below:
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 10
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 11
Which of the following are not the major cause of biodiversity loss in a geographical region?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 11
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 12
A number of human/natural activities contribute to deforestation which includes
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 12
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 13
Deforestation is not a direct cause of:
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 13
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 14
Which of the following chemicals is mainly responsible for ozone depletion?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 14
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 15
The rain is called as acid rain, when its pH is less than_____.
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 15
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 16
The adverse effect(s) of acid rain is(are)
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 16
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 17
Which of the following convention is related to ozone depletion?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 17
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 18
Which of the following is most harmful for ozone depletion?
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 18
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 19
Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 20
Acid rain is caused due to ________.
Detailed Solution for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) - Question 20
Information about Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Environmental Awareness (Environmental Issues), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF