Test: Environmental Awareness (Introduction & Basics) - Software Development MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Environmental Awareness (Introduction & Basics)
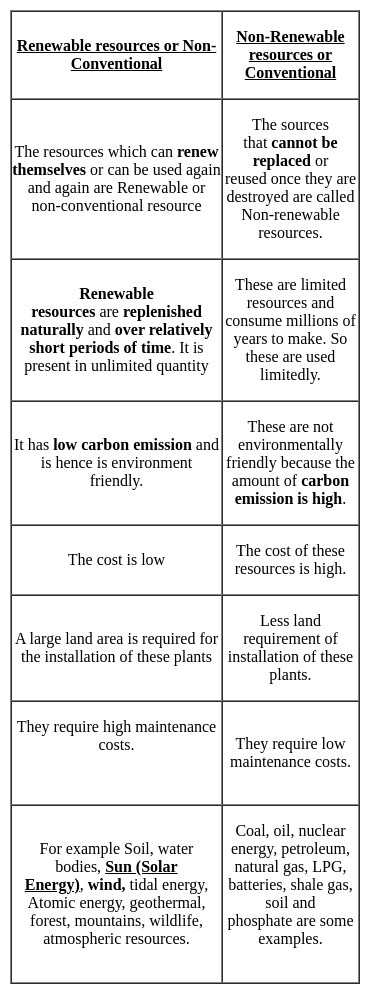
Which of the following is a renewable energy source?
The main purpose of rainwater harvesting is recharge the
Consider the following statements with respect to Ecological Pyramid:
1. The pyramid of biomass in a sea is generally inverted.
2. The pyramid of energy in any ecosystem can never be inverted.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following is the most stable ecosystem?
______ is the concentration of a toxin at successively higher levels in a food chain.
Which option is correct, when we only accomplish two out of three pillars of Sustainable Development?
Consider the following:
1. Kulhs
2. Khadin
3. Johads
4. Madakas
5. Ahar
Which of the following are Rainwater Harvesting methods?
Solar energy, Geothermal energy, tidal energy are ________.
What will happen if all the deer are killed in the given food chain?
Grass → Deer → Lion
Assertion (A): Deforestation and constructional activities causes the extinction of wild animals
Reason (R): Due to loss of natural habitats, animal species become vulnerable or endangered
Choose the correct answer from the codes given below:
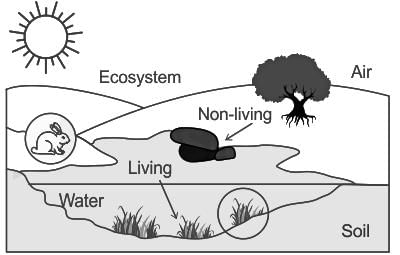
Which of the following is not correct about ecosystem?
Select the correct sequence of tropic levels with increasing potential energy
These are the methods of water conservation, identity which of these are the right process for conservation -
1. Using drip irrigation by farmers.
2. Rainwater is collected by pipes and stored in tanks.
3. Using more water to clean the toilets and washrooms.
4. Water saving habits are introduced to small children.
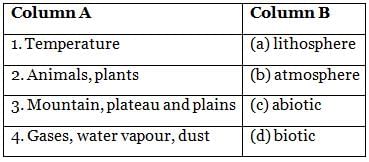
Match the contents of Column A with that of Column B.
Chronologically arrange the following sources in the order they connected through the 'hydrological cycle' (from first to last)