Test: Environmental Awareness (Wastes) - Software Development MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Environmental Awareness (Wastes)
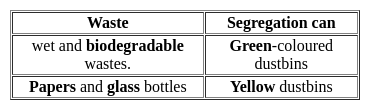
Select the incorrect match in terms of correct waste management practices.
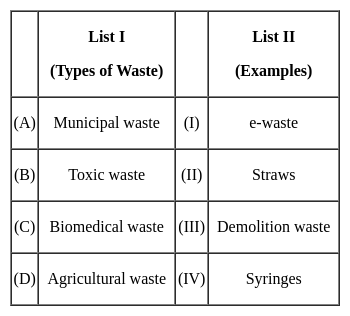
Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
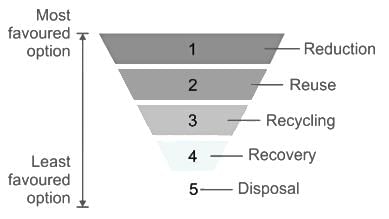
Waste management has been one of the most current issues being tackled at present. Which of the following is a good example for it?
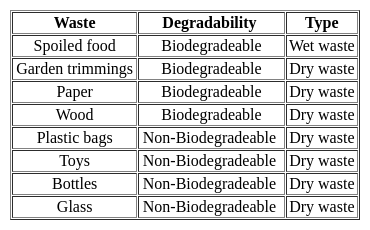
Rani separated her waste into two groups.
Group 1: spoiled food, garden trimmings, paper, wood
Group 2: plastic bags, toys, bottles, glass
This segregation is on the basis of:
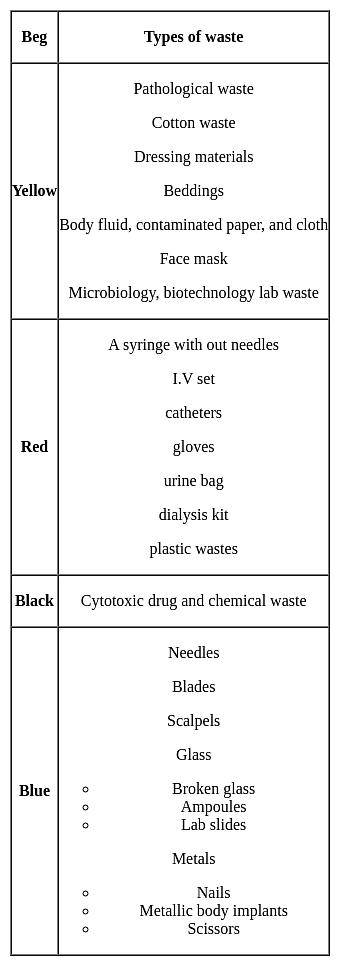
Needles, syringes, scalpels and blades are disposed in:
Name the law in India which deals with waste management.
Which of the following is likely a characteristic of hazardous waste?
The biggest obstacle in managing municipal solid wastes in India is:
When is International E-Waste Day observed every year?
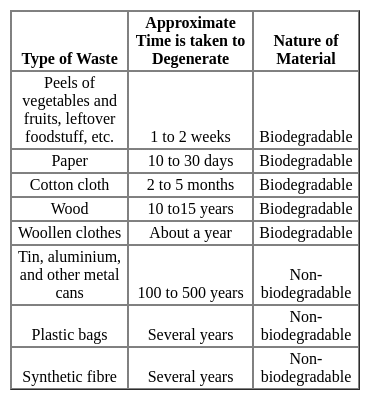
Which of the following materials CANNOT be recycled?
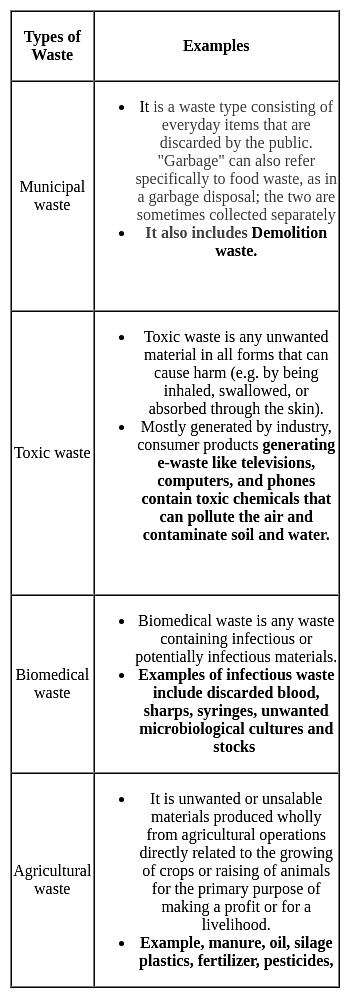
Which type of waste is classified as hazardous ?