Test: Features Of The Indian Constitution - SSC MTS / SSC GD MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test General Awareness for SSC Exams - Test: Features Of The Indian Constitution
Which of the following accurately describes the basic structure doctrine of the Constitution of India?
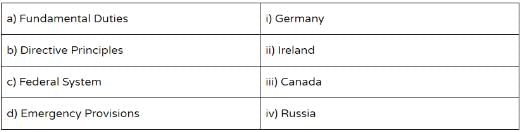
Match the provisions in the Constitution of India with respective countries from where they have been borrowed –

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The preamble in the Constitution of India has been borrowed from
Which of the following is not a Constitutional position in India?
Consider the following statements about Westminster System –
(i) The head of the State is also the executive head.
(ii) Council of ministers is responsible to the head of the State.
Which of the above statements is/are CORRECT?
The Constitution of India has borrowed the concept of ‘Procedure Established by Law’ from
The provisions related to the amendment of the Constitution of India have been borrowed from
Which part of the Constitution of India deals with the fundamental rights?
Which of the following is/are basic features of the Constitution of India ?
(i) Fundamental Rights
(ii) Parliamentary form of government
(iii) Distribution of taxation power between the Union and the states
(iv) Three tier governance
How many Schedules are currently there in the Constitution of India?
|
233 videos|309 docs|52 tests
|
|
233 videos|309 docs|52 tests
|

















