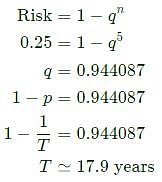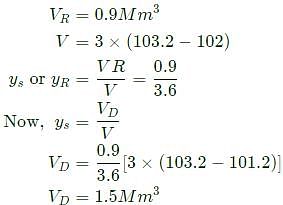Test: Flood Routing and Flood Control - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Engineering Hydrology - Test: Flood Routing and Flood Control
A culvert is designed for a flood frequency of 100 years and a useful life of 20 years. The risk involved in the design of the culvert (in percentage up to two decimal places)
A flood control structure having an expected life of n years is designed by considering a flood of return period T years. When T = n, and n → ∝, the structure's hydrologic risk of failure in percentage is . (round off to one decimal place)
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The probability that the annual maximum flood discharge will exceed 25000 m3/s, at least once in next 5 years is found to be 0.25. The return period of this flood event (in years, round off to 1 decimal place) is ____
For routing of flood in a given channel using the Muskingum method, two of the routing coefficients are estimated as C0 = -0.25 and C1 = 0.55. The value of the third coefficient C2 would be ______
The Muskingum Model of routing a flood through a stream reach is expressed as 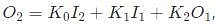 where K0, K1 and K2 are the routing coefficients for the concerned reach, I1 and I2 are the inflows to reach, and O1 and O2 are the outflows from the reach corresponding to time step 1 and 2 respectively. The sum of K0, K1 and K2 of the model is
where K0, K1 and K2 are the routing coefficients for the concerned reach, I1 and I2 are the inflows to reach, and O1 and O2 are the outflows from the reach corresponding to time step 1 and 2 respectively. The sum of K0, K1 and K2 of the model is
A conventional flow duration curve is a plot between
When the outflow from a storage reservoir is uncontrolled as in a freely operating spillway, the peak of outflow hydrograph occurs at
The stage-discharge relation in a river during the passage of flood is measured. If qf is the discharge at the stage when water surface is falling and qr is the discharge at the same stage when water surface is rising, then
A flood wave with a known inflow hydrograph is routed through a large reservoir. The outflow hydrograph will have
A 1-h rainfall of 10 cm magnitude at a station has a return period of 50 years. The probability that a 1-h rainfall of magnitude 10 cm or more will occur in each of two successive years is:
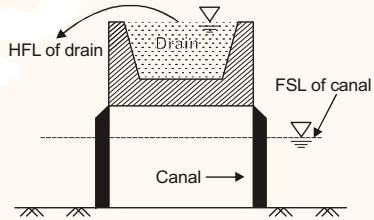
Superpassage is a canal cross-drainage structure in which
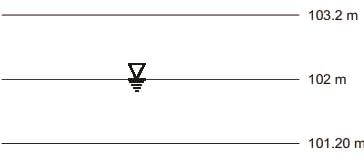
In a homogeneous unconfined aquifer of area 3.00km2, the water table was at an elevation of 102.00 m. After a natural recharge of volume 0.90 million cubic meter (Mm2), the water table rose to 103.20 m. After this recharge, ground water pumping took place and the water table dropped down to 101.020 m. The volume of ground water pumped after the natural recharge, expressed (in Mm2 and round off to two decimal places), is ______.
|
20 videos|36 docs|30 tests
|
|
20 videos|36 docs|30 tests
|