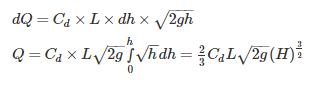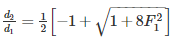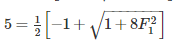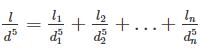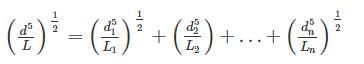Test: Fluid Mechanics- 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test SSC JE Civil Engineering 2025 Mock Test Series - Test: Fluid Mechanics- 2
Specific gravity of water is 1.0 which is reported at a temperature of:
For a uniform flow with depth of 0.6 m and Froude number of 2.0 in a rectangular channel, the specific energy will be -
The major loss of hydraulic energy in pipe flow occurs in long pipe due to:-
For a vacuum pressure of 4.5 m of water, the equivalent absolute pressure is:
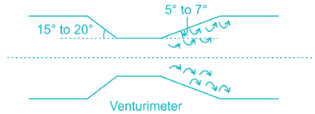
In order, to avoid separation in Venturi meter the angle of divergence is kept
The specific speed of a pump is defined as the speed of a unit of such a size that it discharge:
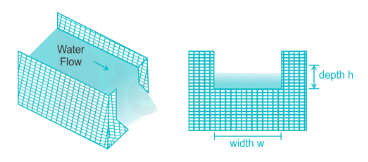
The discharge over a sharp - edged rectangular notch of width w depth h is equal to
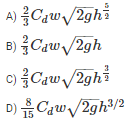
The point at which the resultant pressure on a immersed surface acts, is known as:
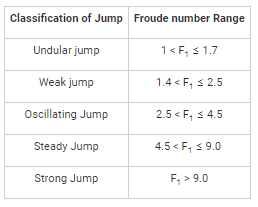
The sequent depth ratio in a hydraulic jump termed in a horizontal rectangular channel is 5. The Froude number of the supercritical stream is
The flow of water in a wash hand basin when it is being emptied through a central opening, is an example of
A compound pipe of diameters d1, d2 and d3 having length l1, l2 and l3 respectively is to be replaced by an equivalent pipe of uniform diameter d and length l. The size of the equivalent pipe is given by
The equation 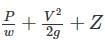 Zconstant is based on the following assumptions regarding the flow of fluid
Zconstant is based on the following assumptions regarding the flow of fluid
|
1 videos|1 docs|64 tests
|



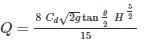
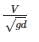
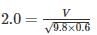
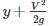
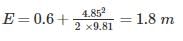
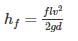
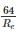
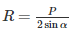
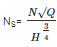 where Q=discharge, H=head, Ns= specific speed, N= speed of pump.
where Q=discharge, H=head, Ns= specific speed, N= speed of pump.