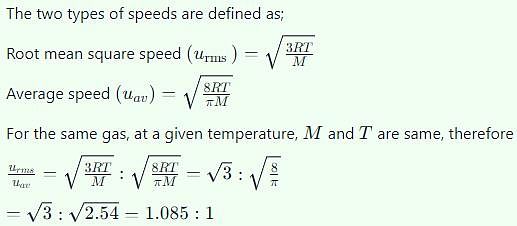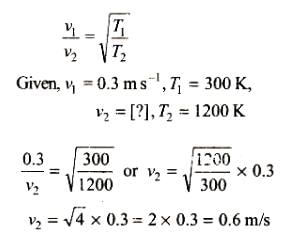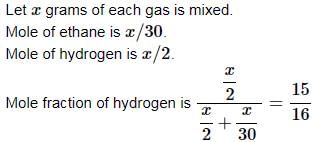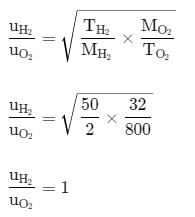Test: Gaseous State - 1 - Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Physical Chemistry - Test: Gaseous State - 1
The ratio of root mean square velocity to average velocity of a gas molecule at a particular temperature is:
The temperature at which a real gas obeys the ideal gas laws over a wide range of pressure is:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Equal weights of methane and oxygen and mixed in an empty container at 25°C. The fraction of the total pressure exerted by oxygen is:
Helium atom is two times heavier than a hydrogen molecule. At 298 K, the average kinetic energy of a helium atom is:
No cooling occurs, when an ideal gas undergoes unrestrained expansion, because the molecules:
A liquid is in equilibrium with its vapour at it’s boiling point. On the average, the molecules in the two phases have equal:
The average velocity of an ideal gas molecule at 27°C is 0.3 m/s. The average velocity at 927°C will be
In van der Waals’ equation of state for a non-ideal gas, the term that accounts for intermolecular forces is:
A bottle of dry ammonia and a bottle of dry hydrogen chloride connected through a long tube are opened simultaneously at both ends the white ammonium chloride ring first formed will be:
The value of van der Waals’ constant ‘a’ for the gases O2, N2, NH3 and CH4 are 1.360, 1.390, 4.170 and 2.253 L2 atm mol–2 respectively. The gas which can most easily be liquefied is:
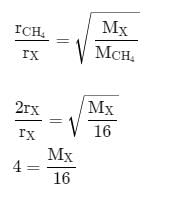
The rate of diffusion of methane at a given temperature is twice that of a gas X. The molecular weight of X is:
According to kinetics theory of gases, for a diatomic molecule:
At constant volume, for a fixed number of moles of a gas the pressure of the gas increases with rise of temperature due to:
Equal weights of ethane and hydrogen are mixed in an empty container at 25°C. The fraction of the total pressure exerted by hydrogen is:
The ratio between the root mean square speed of H2 at 50 K and that of O2 at 800 K is:
The critical temperature of water is higher than that of O2 because the H2O molecule has:
According to Graham’s law, at a given temperature the ratio of the rates of diffusionof gases A and B is given by (where, p and M are pressure and molecular weights of gases A and B respectively)
|
83 videos|142 docs|67 tests
|