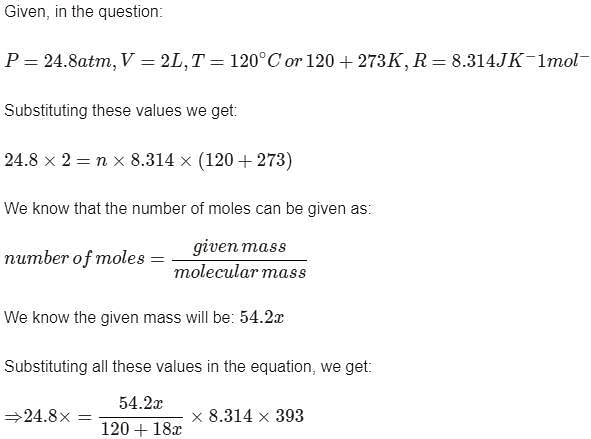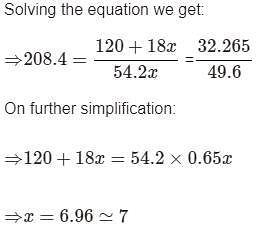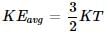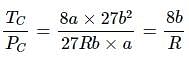Test: Gaseous State - 5 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Physical Chemistry - Test: Gaseous State - 5
A particle is moving in one dimensional box between x = a and x = b. The potential energy is such that the particle can not be outside these limits and the wave function in between is ψ = 4/x. The average value of x is:
Volume of the air that will be expelled from a vessel of 300 cm3 when it is heated from 27°C to 37°C at the same pressure will be:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
2.8 g of a gas at 1 atm and 273 K occupies a volume of 2.24 litres, the gas can not be:
Calculate the volume of O2 at 1 at m and 273 K required for the complete combustion of 2.64 L of acetylene (C2H2) at 1 atm and 273 K. 2C2H2(g) + 5O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 2H2O(l)
A certain hydrate has the formula MgSO4.xH2O. a quantity of 54.2 g of the compound is heated in an over to drive off the water. If the steam generated exerts a pressure of 24.8 atm in a 2.0 L container at 120°C, calculate x:
A high altitude balloon contains 6.81 g of helium in 1.16 × 104 L at –23°C. Assuming ideal gas behaviour, how many grams of helium would have to be added to increase the pressure to 4.0 × 10–3 atm:
Starting out on a trip into the mountains, you inflate the tires on your automobile to a recommended pressure of 3.21 × 105 Pa on a day when the temperature is –5°C. You drive to the beach, where the temperature is 28.0°C. Assume that the volume of the tire has increased by 3%. What is the final pressure in the tyres:
Two glass bulbs A and B at same temperature are connected by a very small tube having a stop-cork. Bulb A has a volume of 100 cm3 and contained the gas while bulb B was empty. On opening the stop-cork, the pressure fell down to 20%. The volume of the bulb B is:
Two closed vessel A and B of equal volume of 8.21 L are connected by a narrow tube of negligible volume with open valve. The left hand side container is found to contain 3 mole CO2 and 2 mole of He at 400 K, what is the partial pressure of He in vessel B at 500 K:
56 g of nitrogen and 96 g of oxygen are mixed isothermally and at a total pressure of 10 at m. The partial pressures of oxygen and nitrogen (in atm) are respectively:
Oxygen gas generated by the decomposition of potassium chlorate is collected over water. The volume of oxygen collected at 24°C and atmospheric pressure of 760 mmHg is 128 mL. Calculate the mass of oxygen gas obtained. The pressure of the water vapour at 24°C is 22.4 mmHg:
Consider three one-litre flasks labeled A, B and C filled with the gases NO, NO2 and N2O, respectively, each at 1 atm and 273 K. In which flask do the molecules have the highest average kinetic energy:
Two flasks A and B have equal volumes. A is maintained at 300 K and B at 600 K, while A contains H2 gas, B has an equal mass of CO2 gas. Find the ratio of total K.E. of gases in flask A to that of B:
A mixture of Ne and Ar at 250 K has a total K.E. = 3 kJ in a closed vessel, the total mass of Ne and Ar is 30 g. Find mass % of Ne in gaseous mixture at 250 K
The most probable speed of 8 g of H2 200 ms–1 average kinetic energy (neglect rotational and vibrational energy) of H2 gas is:
The root mean square speed of 8 g of He is 300 ms–1. Total kinetic energy of He gas is:
The ratio among most probable velocity, mean velocity and root mean square velocity is given by:
Calculate relative rate of effusion of O2 to CH4 through a container containing O2 and CH4 in 3:2 mass ratio:
Calculate γ (ratio of Cp and Cv) for triatomic linear gas at high temperature. Assume that the contribution of vibrational degree of freedom is 75%:
If one mole each of a monoatomic and diatomic gases are mixed at low temperature then Cp/Cv ratio for the mixture is:
At low pressures, van der Waal’s equation is written as The compressibility factor is then equal to:
The temperature at which the second virial coefficient of real gas is zero is called:
A mixture of NH3(g) and N2H4(g) is placed in a sealed container at 300 K. The total pressure is 0.5 atm. The container is heated to 1200 K at which time both substances decompose completely according to the equations
After decomposition is complete, the total pressure at 1200 K is found to be 4.5 atm. Find the mole % of N2H4 in the original mixture:
A given volume of ozonised oxygen (containing 60% oxygen by volume) required 220 sec to effuse which an equal volume of oxygen took 200 sec only under the conditions. If density of O2 is 1.6 g/L then find density of O3:
The van der Waal’s constant ‘b’ of a gas is 4π × 10–4 L/mol. How near can the centres of the two molecules approach each other? [Use: NA = 6 × 1023]
At a constant pressure, what should be the percentage increase in the temperature in Kelvin for a 10% increase in volume:
For a real gas (mol. mass = 60) if density at critical point is 0.80 g/cm3 and its van der Waal’s constant a (in at m L2 mol–2) is:
A mixture of nitrogen and water vapours is admitted to a flask at 760 torr which contains a sufficient solid drying agent after long time the pressure reached a steady value of 722 torr. If the experiment is done at 27°C and drying agent increases in weight by 0.9 gm, what is the volume of the flask? Neglect any possible vapour of drying agent and volume occupied by drying agent:
Vander Waal’s gas equation can be reduced to virial equation and virial equation (in terms of volume)
Where A = first virial coefficient, B = second virial coefficient, C = third virial coefficient. The third virial coefficient of Hg(g) is 625 (cm2/mol)2. What volume is available for movement of 10 moles He(g) atoms present in 50 L vessel:
|
83 videos|142 docs|67 tests
|