Software Development Exam > Software Development Tests > Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Software Development MCQ
Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Software Development MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry)
Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Software Development exam syllabus.The Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) MCQs are made for Software Development 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) below.
Solutions of Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) questions in English are available as part of our course for Software Development & Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) solutions in
Hindi for Software Development course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Software Development Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) | 10 questions in 12 minutes | Mock test for Software Development preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Software Development Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 1
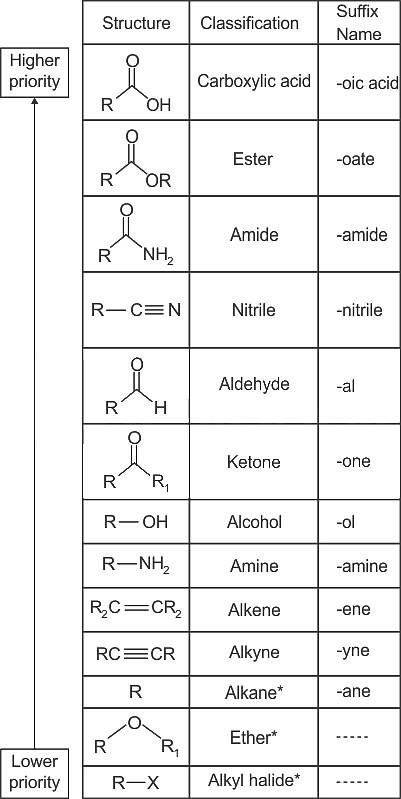
The IUPAC name of the compound CH3 CH2 CH3 is-
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 1
Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 2
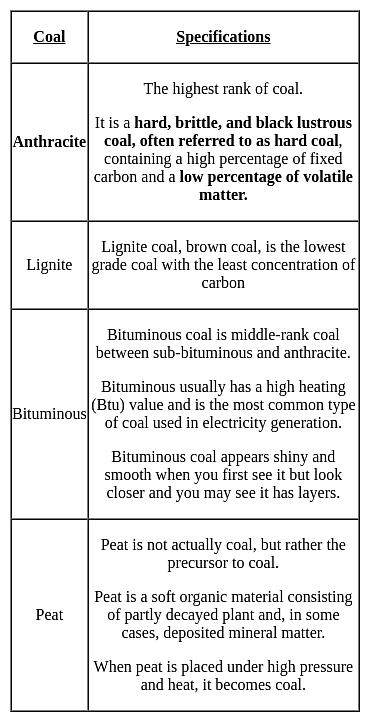
Which type of coal has the highest calorific value?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 2
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 3
Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 4
What is the IUPAC name of compound CH3CH2CHO ?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 4
Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 5
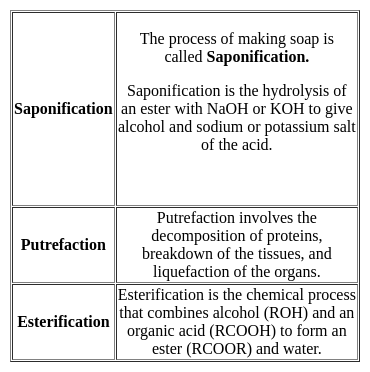
The reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid is called ______.
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 5
Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 6
The stench due to leakage from LPG cylinder because of :
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 6
Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 7
Excessive consumption of alcoholic drinks causes damage to the
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 7
Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 8
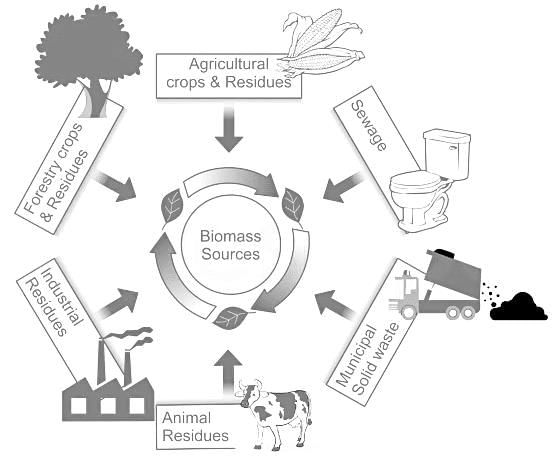
Which of the following is NOT an example of a biomass energy source?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 8
Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 9
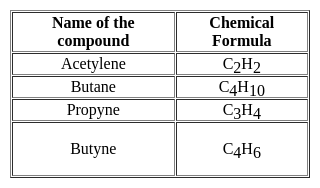
What is the molecular formula of Butane?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 9
Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 10
The souring of milk to curd is an example of
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) - Question 10
Information about Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: General Science (Organic Chemistry), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF