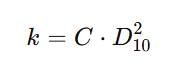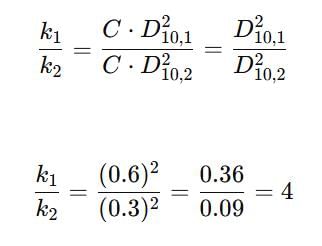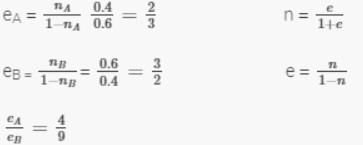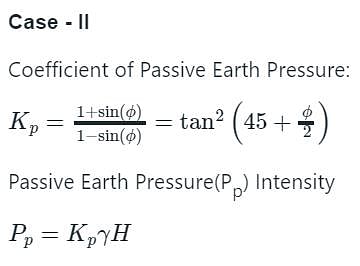Test: Geotechnical Engineering- 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test GATE Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Mock Test Series - Test: Geotechnical Engineering- 2
Given soil sample:
Degree of saturation = 90%
Specific gravity of soil grains = 2.70
Void ratio = 0.30
The water content of the sample is ________ %.
Specific gravity of soil grains = 2.70
Void ratio = 0.30
The water content of the sample is ________ %.
The approximate ratio of the permeability of two clean soils having D10 = 0.6 mm and D10 = 0.3 mm is __________.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Two soil samples A and B have porosities nA = 40% and nB = 60% respectively. What is the ratio of void ratio eA : eB ?
Which one of the following equation correctly gives the relationship between the specific gravity of soil grains (G) and the hydraulic gradient (i) of initiate “quick” condition in sand having a void ratio of 0.5?
If the time required for 60% consolidation of a remoulded soil sample of clay with simple drainage is t, then what is the time required to consolidation the same sample of clay with the same degree of consolidation but with double drainage?
If s is the shear strength, c andare shear strength parameters, and σn is the normal stress at failure, then Coulomb’s equation for shear strength of the soil can be represented by
A wet soil mass is having one-sixth of its volume as air and one-third of its volume as water. The void ratio of the soil is
A soil has liquid limit of 60% plastic limit of 35% and shrinkage limit of 20% and it has a natural moisture content of 50%. The liquidity index of soil is
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Negative skin friction on a pile under vertical compressive load acts
Two footings, one circular and the other square, are founded on the surface of a purely cohensionless soil. The diameter of the circular footing is same as that of the side of the square footing. The ratio of their ultimate bearing capacities is
The liquid limit and plastic limit of sample are 65% and 29% respectively. The percentage of the soil fraction with grain size finer than 0.002 mm is 24. The activity ratio of the soil sample is
A concentrated load of 50t act vertically at a point on the soil surface. If Boussinesq’s equation is applied for computation of stress, then the ratio of vertical stresses at depths of 3 m and 5 m, respective, vertically below the point of application of load will be
In a cohension less soil deposit having a unit weight of 1.5 t/m3 and an angle of internal friction of 30°, the active and passive lateral earth pressure intensities (in t/m2) at a depth of 10 m will, respectively, be
A raft of 6 m × 9 m is found at a depth of 3 m in a cohesive soil having c = 120 kN/m3. The ultimate net bearing capacity of the soil using the Terzaghi’s theory will be nearly
A stratus of 3.5m thick fine sand has a void ratio of 0.7 and G of 2.7. For a quick sand condition to develop in this stratum, the water flowing in upward direction would require a head of
The settlement analysis for a clay layer draining from top and bottom shows a settlement of 2.5 cm in 4 years and an ultimate settlement of 10 cm. However, detailed subsurface investigation reveals that there is non drainage at the bottom. The ultimate settlement in this condition will be ______ cm.
A strip footing having 1.5 m width founded at a depth of 3m below ground level in a clay soil having c = 20 kN/m2. ϕ = 0° and unit weight γ = 20 kN/m3. What is the net ultimate bearing capacity using Skempton’s analysis?
A retaining wall with a vertical back of height 7.32 m supports a cohesionless soil of unit weight 17.3 kN/m3 and an angle of shearing resistance= 300. Given the surface of the soil is horizontal.
Q.
The coefficient of active earth pressure, using Rankine theory, will be
A retaining wall with a vertical back of height 7.32 m supports a cohesionless soil of unit weight 17.3 kN/m3 and an angle of shearing resistance= 300. Given the surface of the soil is horizontal.
Q.
The active thrust per meter of wall using Rankine theory is
|
31 docs|280 tests
|
|
31 docs|280 tests
|