Test: Governance in India - UGC NET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Governance in India
When was rural local governance institutionalized in India?
Infrastructure aspects provided by the Government of India in formation of National e-Governance Plan for storage of data and hosting applications, network connectivity and capacity building respectively are
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
A. Digital governance has been legalized by the IT Act (2000) in India.
B. IT Act is a watershed in conceptualizing administrative reforms in India.
C. Digital governance is a boon in curbing bureaucratic red-tapism.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which is the Act which provides legal framework for e-Governance in India
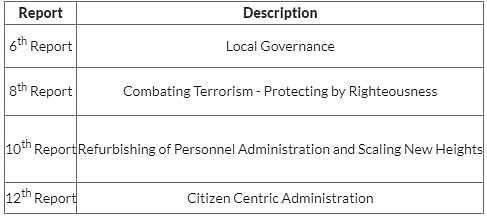
In which report of the Second Administrative Reforms Commission has identified "Citizen-Centric Administration" as barriers of Good Governance in India?
When we say that we have federal system of governance in India, what does it imply?
Which one of the following is not basic elements of the citizen charter?
Consider the following statements about Panchayati Raj in India:
(a) Panchayati Raj was established in India on the recommendations of Balwant Rai Mehta committee.
(b) Rajasthan was the first state to establish Panchayati Raj in 1959.
(c) Panchayati Raj system has been implemented in all the states of the country.
(d) Panchayati Raj functions as a system of governance in which gram panchayats are the basic units of local administration.
Select the correct statements using the code below:
The national initiative named 'Kayakalp' was launched by which ministry ?