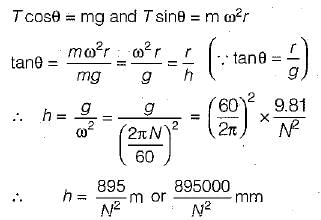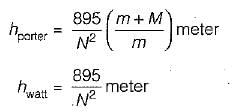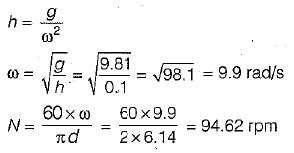Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Tests > Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering > Test: Governors - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Test: Governors - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering - Test: Governors - 1
Test: Governors - 1 for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Test: Governors - 1 questions and answers have been
prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus.The Test: Governors - 1 MCQs are made for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Governors - 1 below.
Solutions of Test: Governors - 1 questions in English are available as part of our Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering for Mechanical Engineering & Test: Governors - 1 solutions in
Hindi for Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Governors - 1 | 10 questions in 30 minutes | Mock test for Mechanical Engineering preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering for Mechanical Engineering Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Test: Governors - 1 - Question 1
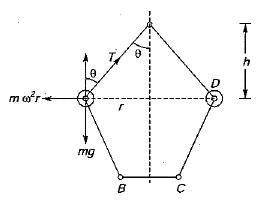
Test: Governors - 1 - Question 2
The ratio of the height of a porter governor to that of a Watt governoer when the lengths of the links and the arms are same is
Detailed Solution for Test: Governors - 1 - Question 2
Test: Governors - 1 - Question 3
In a governor, if the equilibrium speed is constant for all radii of rotation of balls, the governor is said to be
Detailed Solution for Test: Governors - 1 - Question 3
Test: Governors - 1 - Question 4
The force resisting the outward movement of balls of the governor is known as
Detailed Solution for Test: Governors - 1 - Question 4
Detailed Solution for Test: Governors - 1 - Question 5
Test: Governors - 1 - Question 6
The effort of a governor is the force exerted by the governor on the
Detailed Solution for Test: Governors - 1 - Question 6
Detailed Solution for Test: Governors - 1 - Question 7
Detailed Solution for Test: Governors - 1 - Question 8
Detailed Solution for Test: Governors - 1 - Question 9
Test: Governors - 1 - Question 10
For a Watt governor, 10 cm height corresponds to an speed of about
Detailed Solution for Test: Governors - 1 - Question 10
|
45 videos|314 tests
|
Information about Test: Governors - 1 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Governors - 1 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Governors - 1, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice