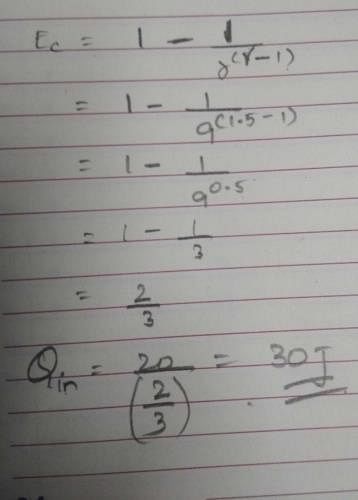Test: Heat Engine(6 Sep) - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for JEE Preparation - Test: Heat Engine(6 Sep)
In a heat engine the ratio of net work done per cycle by the engine to the total amount of heat absorbed per cycle by the working substance from the source is known as
In actual home refrigerator vapours of Freon ( which is dichlorodifluoro methane CCl2F2) act as
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A carnot engine is taking 700 cal from source and is rejecting 500 cal to the sink in each cycle. What is the temperature of sink if the source temperature is 150° C .
According to Carnot theorem no heat engine working between two given temperatures of source and sink can be more efficient than a perfectly ___________ engine working between the same two temperatures
How much heat energy a petrol engine would require to do 20 kWh of work? Its adiabatic compression ratio is 9 and γ= 1.5.
An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (Fig.). Four processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. Out of 1, 2, 3 and 4 which one is adiabatic.

What would be the horse power of a steam engine with average pressure of steam 9x 104 Nm-2 , the area of cross section of the piston is 0.2 m2, length of stroke is 0.6 m and piston makes 5 revolutions per second?
The ratio of quantity of heat removed per cycle from the contents of the refrigerator to the energy spent per cycle to remove this heat is called the
In a Carnot engine 800 J of heat is absorbed from a source at 400 K and 640 J of heat is rejected to the sink. The temperature of the sink is:
The temperature inside a refrigerator is 4°C and the room temperature is 27°C. How many joules of heat will be delivered to the room for each joule of electricity consumed by the refrigerator?( Treat the refrigerator as ideal).
|
360 tests
|