Test: IPv4 - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Computer Networks - Test: IPv4
An organization requires a range of IP addresses to assign one to each of its 1500 computers. The organization has approached on Internet Service Provider (ISP) for this task. The ISP uses CIDR and serves the requests from the available IP address space 202.61.0.0/17. The ISP wants to assign an address space to the organization which will minimize the number of routing entries in the ISP’s router using route aggregation. Which of the following address spaces are potential candidates from which the ISP can allot any one to the organization?
I. 202.61.84.0/21
II. 202.61.104.0/21
III. 202.61.64.0/21
IV. 202.61.144.0/21
I. 202.61.84.0/21
II. 202.61.104.0/21
III. 202.61.64.0/21
IV. 202.61.144.0/21
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
There is an Ethernet port on a router were assigned an IP address of 172.16.112.1/25. Which of the following would be the valid subnet address of this host?
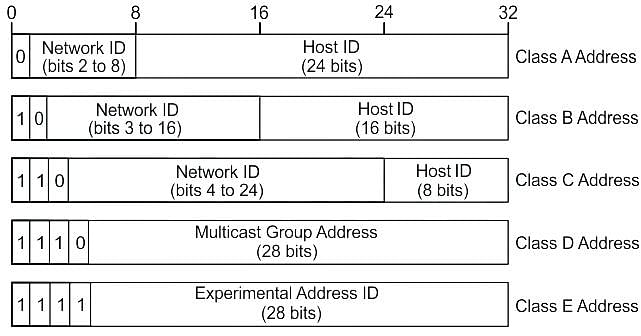
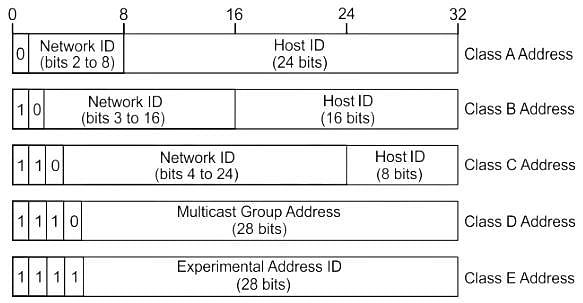
An IPv4 address is a __________ address, which is categorised into different IP classes.
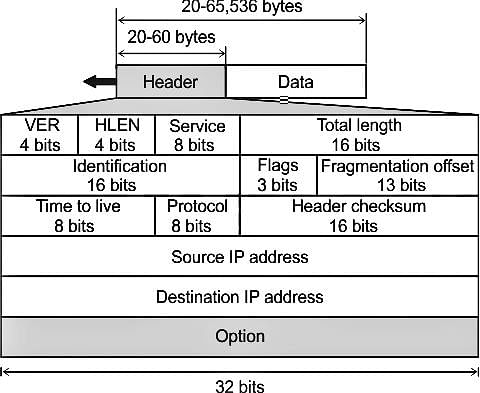
An IP packet has arrived with the first 8 bits as 0100 0010. Which of the following is correct ?
Your router has the following IP address an Ethenet 0: 172.16.2.1/23. Which of the following can be valid host IDs on the LAN interface attached to the router?
1. 172.16.1.100
2. 172.16.1.198
3. 172.16.2.255
4. 172.16.3.0
|
21 videos|113 docs|66 tests
|
|
21 videos|113 docs|66 tests
|