Test: India and its Foreign Policy - UGC NET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: India and its Foreign Policy
What does Article 42 of the Indian Constitution deals with?
Consider the following statements regarding the Act East policy:
I. It is the successor to the Look East policy.
II. The Indian economy has huge benefits from Act East strategy.
Which of the above statements is/ are correct?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following is correctly matched.
(A) SAARC - Kathmandu
(B) Act East Policy - Narasimha Rao
(C) Neighbourhood first policy - Narendra Modi
(D) Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank - Kualalampur
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Arrange the following foundational elements of Indian foreign policy in order of their appearance:
(A) Gujaral doctrine
(B) Panchasheel
(C) Look East policy
(D) Indo-Soviet Treaty of Friendship
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
What are the core values of Indian Foreign Policy?
A. Blend of idealism and realism
B. Value of Tolerance
C. Anti-imperialism and anti-colonialism
D. Territorial Expansion
E. Neighbourhood First Diplomacy
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
There are two statements, one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R):
Assertion (A): India is now more aware of its own capabilities and the expectations that the world has of India.
Reason (R): One of the reasons is that India’s policy of Non-Alignment has turned into Multi Alignment.
Choose the correct option:
There are two statements, one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R):
Assertion (A): SAGAR is the strategic vision launched by India in 2015 for enhancing maritime cooperation in the Indian Ocean region.
Reason (R): India's goal with SAGAR is to strengthen economic and security connections with its maritime neighbours while also assisting in the development of its maritime security capabilities.
Choose the correct option:
Match List I with List II
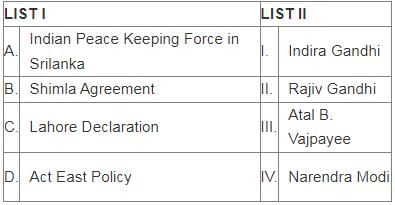
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Read the statements (A) and (R) and choose the correct option.
Assertion (A) - There was considerable unease in Indo-US relations during the 1950s.
Reason (R) - The US was not happy about India’s policy of non-alignment.

















